Mathematical series | Real transcendental numbers | Complex analysis | Pi
Pi
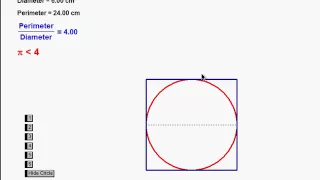
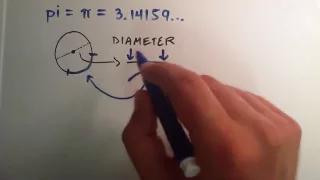
The number π (/paɪ/; spelled out as "pi") is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159. The number π appears in many formulas across mathematics and physics. It is an irrational number, meaning that it cannot be expressed exactly as a ratio of two integers, although fractions such as are commonly used to approximate it. Consequently, its decimal representation never ends, nor enters a permanently repeating pattern. It is a transcendental number, meaning that it cannot be a solution of an equation involving only sums, products, powers, and integers. The transcendence of π implies that it is impossible to solve the ancient challenge of squaring the circle with a compass and straightedge. The decimal digits of π appear to be randomly distributed, but no proof of this conjecture has been found. For thousands of years, mathematicians have attempted to extend their understanding of π, sometimes by computing its value to a high degree of accuracy. Ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians and Babylonians, required fairly accurate approximations of π for practical computations. Around 250 BC, the Greek mathematician Archimedes created an algorithm to approximate π with arbitrary accuracy. In the 5th century AD, Chinese mathematicians approximated π to seven digits, while Indian mathematicians made a five-digit approximation, both using geometrical techniques. The first computational formula for π, based on infinite series, was discovered a millennium later. The earliest known use of the Greek letter π to represent the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter was by the Welsh mathematician William Jones in 1706. The invention of calculus soon led to the calculation of hundreds of digits of π, enough for all practical scientific computations. Nevertheless, in the 20th and 21st centuries, mathematicians and computer scientists have pursued new approaches that, when combined with increasing computational power, extended the decimal representation of π to many trillions of digits. These computations are motivated by the development of efficient algorithms to calculate numeric series, as well as the human quest to break records. The extensive computations involved have also been used to test supercomputers. Because its definition relates to the circle, π is found in many formulae in trigonometry and geometry, especially those concerning circles, ellipses and spheres. It is also found in formulae from other topics in science, such as cosmology, fractals, thermodynamics, mechanics, and electromagnetism. In modern mathematical analysis, it is often instead defined without any reference to geometry; therefore, it also appears in areas having little to do with geometry, such as number theory and statistics. The ubiquity of π makes it one of the most widely known mathematical constants inside and outside of science. Several books devoted to π have been published, and record-setting calculations of the digits of π often result in news headlines. (Wikipedia).