Orthogonal coordinate systems | Three-dimensional coordinate systems
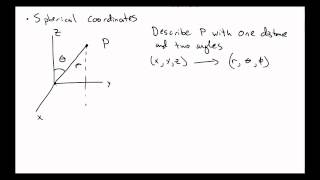
Spherical coordinate system
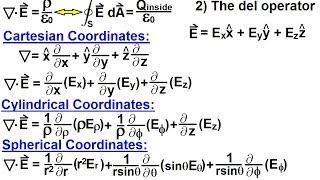
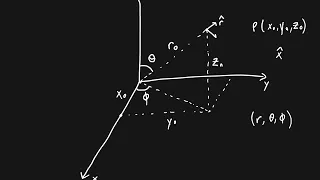
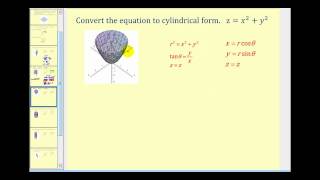
In mathematics, a spherical coordinate system is a coordinate system for three-dimensional space where the position of a point is specified by three numbers: the radial distance of that point from a fixed origin, its polar angle measured from a fixed zenith direction, and the azimuthal angle of its orthogonal projection on a reference plane that passes through the origin and is orthogonal to the zenith, measured from a fixed reference direction on that plane. It can be seen as the three-dimensional version of the polar coordinate system. The radial distance is also called the radius or radial coordinate. The polar angle may be called colatitude, zenith angle, normal angle, or inclination angle. When radius is fixed, the two angular coordinates make a coordinate system on the sphere sometimes called spherical polar coordinates. The use of symbols and the order of the coordinates differs among sources and disciplines. This article will use the ISO convention frequently encountered in physics: gives the radial distance, polar angle, and azimuthal angle. By contrast, in many mathematics books, or gives the radial distance, azimuthal angle, and polar angle, switching the meanings of θ and φ. Other conventions are also used, such as r for radius from the z-axis, so great care needs to be taken to check the meaning of the symbols. According to the conventions of geographical coordinate systems, positions are measured by latitude, longitude, and height (altitude). There are a number of celestial coordinate systems based on different fundamental planes and with different terms for the various coordinates. The spherical coordinate systems used in mathematics normally use radians rather than degrees and measure the azimuthal angle counterclockwise from the x-axis to the y-axis rather than clockwise from north (0°) to east (+90°) like the horizontal coordinate system. The polar angle is often replaced by the elevation angle measured from the reference plane towards the positive Z axis, so that the elevation angle of zero is at the horizon; the depression angle is the negative of the elevation angle. The spherical coordinate system generalizes the two-dimensional polar coordinate system. It can also be extended to higher-dimensional spaces and is then referred to as a hyperspherical coordinate system. (Wikipedia).