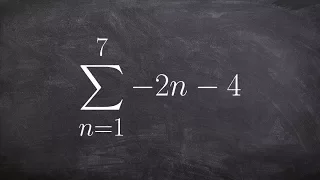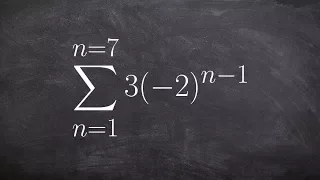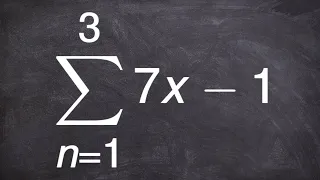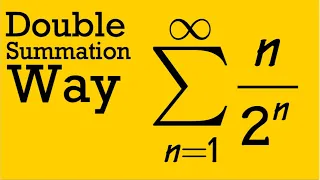Mathematical notation | Addition
Summation
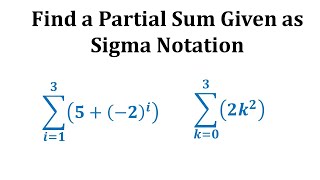
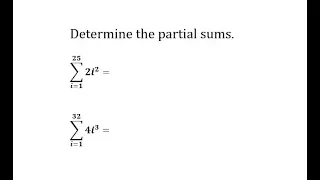
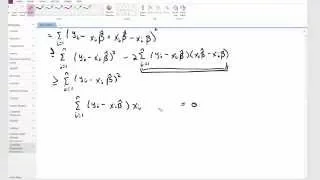
In mathematics, summation is the addition of a sequence of any kind of numbers, called addends or summands; the result is their sum or total. Beside numbers, other types of values can be summed as well: functions, vectors, matrices, polynomials and, in general, elements of any type of mathematical objects on which an operation denoted "+" is defined. Summations of infinite sequences are called series. They involve the concept of limit, and are not considered in this article. The summation of an explicit sequence is denoted as a succession of additions. For example, summation of [1, 2, 4, 2] is denoted 1 + 2 + 4 + 2, and results in 9, that is, 1 + 2 + 4 + 2 = 9. Because addition is associative and commutative, there is no need of parentheses, and the result is the same irrespective of the order of the summands. Summation of a sequence of only one element results in this element itself. Summation of an empty sequence (a sequence with no elements), by convention, results in 0. Very often, the elements of a sequence are defined, through a regular pattern, as a function of their place in the sequence. For simple patterns, summation of long sequences may be represented with most summands replaced by ellipses. For example, summation of the first 100 natural numbers may be written as 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + ⋯ + 99 + 100. Otherwise, summation is denoted by using , where is an enlarged capital Greek letter sigma. For example, the sum of the first n natural numbers can be denoted as For long summations, and summations of variable length (defined with ellipses or Σ notation), it is a common problem to find closed-form expressions for the result. For example, Although such formulas do not always exist, many summation formulas have been discovered—with some of the most common and elementary ones being listed in the remainder of this article. (Wikipedia).