Momentum
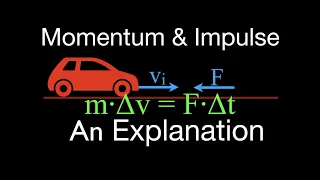
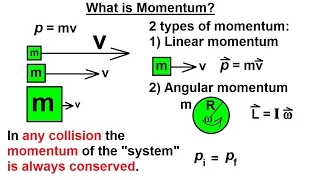
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If m is an object's mass and v is its velocity (also a vector quantity), then the object's momentum p is : In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement of momentum is the kilogram metre per second (kg⋅m/s), which is equivalent to the newton-second. Newton's second law of motion states that the rate of change of a body's momentum is equal to the net force acting on it. Momentum depends on the frame of reference, but in any inertial frame it is a conserved quantity, meaning that if a closed system is not affected by external forces, its total linear momentum does not change. Momentum is also conserved in special relativity (with a modified formula) and, in a modified form, in electrodynamics, quantum mechanics, quantum field theory, and general relativity. It is an expression of one of the fundamental symmetries of space and time: translational symmetry. Advanced formulations of classical mechanics, Lagrangian and Hamiltonian mechanics, allow one to choose coordinate systems that incorporate symmetries and constraints. In these systems the conserved quantity is generalized momentum, and in general this is different from the kinetic momentum defined above. The concept of generalized momentum is carried over into quantum mechanics, where it becomes an operator on a wave function. The momentum and position operators are related by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. In continuous systems such as electromagnetic fields, fluid dynamics and deformable bodies, a momentum density can be defined, and a continuum version of the conservation of momentum leads to equations such as the Navier–Stokes equations for fluids or the Cauchy momentum equation for deformable solids or fluids. (Wikipedia).