Articles containing proofs | Irrational numbers
Irrational number
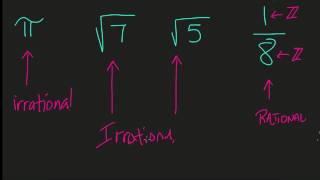
In mathematics, the irrational numbers (from in- prefix assimilated to ir- (negative prefix, privative) + rational) are all the real numbers that are not rational numbers. That is, irrational numbers cannot be expressed as the ratio of two integers. When the ratio of lengths of two line segments is an irrational number, the line segments are also described as being incommensurable, meaning that they share no "measure" in common, that is, there is no length ("the measure"), no matter how short, that could be used to express the lengths of both of the two given segments as integer multiples of itself. Among irrational numbers are the ratio π of a circle's circumference to its diameter, Euler's number e, the golden ratio φ, and the square root of two. In fact, all square roots of natural numbers, other than of perfect squares, are irrational. Like all real numbers, irrational numbers can be expressed in positional notation, notably as a decimal number. In the case of irrational numbers, the decimal expansion does not terminate, nor end with a repeating sequence. For example, the decimal representation of π starts with 3.14159, but no finite number of digits can represent π exactly, nor does it repeat. Conversely, a decimal expansion that terminates or repeats must be a rational number. These are provable properties of rational numbers and positional number systems, and are not used as definitions in mathematics. Irrational numbers can also be expressed as non-terminating continued fractions and many other ways. As a consequence of Cantor's proof that the real numbers are uncountable and the rationals countable, it follows that almost all real numbers are irrational. (Wikipedia).