Functional analysts | Measure theorists | Mental calculators | Numerical analysts | Operator theorists | Cellular automatists | Lattice theorists
John von Neumann
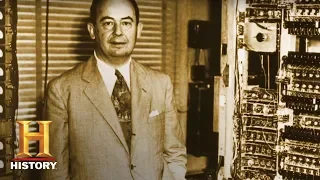
John von Neumann (/vɒn ˈnɔɪmən/; Hungarian: Neumann János Lajos, pronounced [ˈnɒjmɒn ˈjaːnoʃ ˈlɒjoʃ]; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian-American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist, engineer and polymath. He was regarded as having perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time and was said to have been "the last representative of the great mathematicians who were equally at home in both pure and applied mathematics". He integrated pure and applied sciences. Von Neumann made major contributions to many fields, including mathematics (foundations of mathematics, measure theory, functional analysis, ergodic theory, group theory, lattice theory, representation theory, operator algebras, matrix theory, geometry, and numerical analysis), physics (quantum mechanics, hydrodynamics, ballistics, nuclear physics and quantum statistical mechanics), economics (game theory and general equilibrium theory), computing (Von Neumann architecture, linear programming, numerical meteorology, scientific computing, self-replicating machines, stochastic computing), and statistics. He was a pioneer of the application of operator theory to quantum mechanics in the development of functional analysis, and a key figure in the development of game theory and the concepts of cellular automata, the universal constructor and the digital computer. Von Neumann published over 150 papers in his life: about 60 in pure mathematics, 60 in applied mathematics, 20 in physics, and the remainder on special mathematical subjects or non-mathematical ones. His last work, an unfinished manuscript written while he was dying in hospital, was later published in book form as The Computer and the Brain. His analysis of the structure of self-replication preceded the discovery of the structure of DNA. In a shortlist of facts about his life he submitted to the National Academy of Sciences, he wrote, "The part of my work I consider most essential is that on quantum mechanics, which developed in Göttingen in 1926, and subsequently in Berlin in 1927–1929. Also, my work on various forms of operator theory, Berlin 1930 and Princeton 1935–1939; on the ergodic theorem, Princeton, 1931–1932." During World War II, von Neumann worked on the Manhattan Project with theoretical physicist Edward Teller, mathematician Stanislaw Ulam and others, problem-solving key steps in the nuclear physics involved in thermonuclear reactions and the hydrogen bomb. He developed the mathematical models behind the explosive lenses used in the implosion-type nuclear weapon and coined the term "kiloton" (of TNT) as a measure of the explosive force generated. During this time and after the war, he consulted for a vast number of organizations including the Office of Scientific Research and Development, the Army's Ballistic Research Laboratory, the Armed Forces Special Weapons Project and the Oak Ridge National Laboratory. At the peak of his influence in the 1950s he was the chair for a number of critical Defense Department committees including the Nuclear Weapons Panel of the Air Force Scientific Advisory Board and the ICBM Scientific Advisory Committee as well as a member of the influential Atomic Energy Commission. He played a key role alongside Bernard Schriever and Trevor Gardner in contributing to the design and development of the United States' first ICBM programs. During this time he was considered the nation's foremost expert on nuclear weaponry and the leading defense scientist at the Pentagon. As a Hungarian émigré, concerned that the Soviets would achieve nuclear superiority, he designed and promoted the policy of mutually assured destruction to limit the arms race. In honor of his achievements and contributions to the modern world, he was named in 1999 the Financial Times Person of the Century, as a representative of the century's characteristic ideal that the power of the mind could shape the physical world, and of the "intellectual brilliance and human savagery" that defined the 20th century. (Wikipedia).