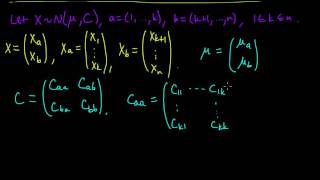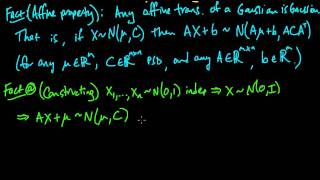Articles containing proofs | Gaussian function | Exponentials
Gaussian function
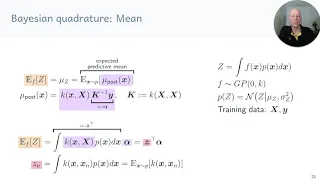
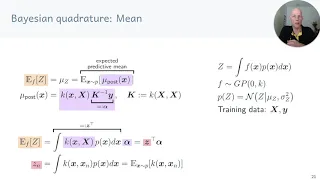
In mathematics, a Gaussian function, often simply referred to as a Gaussian, is a function of the base form and with parametric extensionfor arbitrary real constants a, b and non-zero c. It is named after the mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss. The graph of a Gaussian is a characteristic symmetric "bell curve" shape. The parameter a is the height of the curve's peak, b is the position of the center of the peak, and c (the standard deviation, sometimes called the Gaussian RMS width) controls the width of the "bell". Gaussian functions are often used to represent the probability density function of a normally distributed random variable with expected value μ = b and variance σ2 = c2. In this case, the Gaussian is of the form Gaussian functions are widely used in statistics to describe the normal distributions, in signal processing to define Gaussian filters, in image processing where two-dimensional Gaussians are used for Gaussian blurs, and in mathematics to solve heat equations and diffusion equations and to define the Weierstrass transform. (Wikipedia).