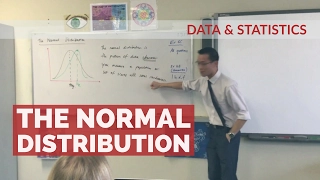
The Normal Distribution (1 of 3: Introductory definition)
More resources available at www.misterwootube.com
From playlist The Normal Distribution

Statistics: Ch 6 The Normal Probability Distribution (8 of 28) Standard Deviation: Example
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! To donate: http://www.ilectureonline.com/donate https://www.patreon.com/user?u=3236071 We will study the example of the normal probability distribution of the height of males over the age of 20 in the US given that mu=5’
From playlist STATISTICS CH 6 THE NORMAL PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION
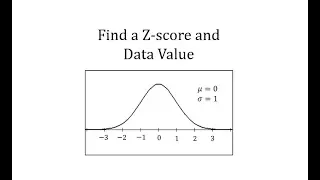
Normal Distribution: Find a Z Score and a Data Value (General)
This video explains how to determine a z-score and how to use a z-score to determine a data value. http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist The Normal Distribution

The Normal Distribution (3 of 3: Basic questions)
More resources available at www.misterwootube.com
From playlist The Normal Distribution

Find the Minimum and Maximum Usual Values
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!! https://goo.gl/JQ8Nys Find the Minimum and Maximum Usual Values
From playlist Statistics

Ex: Linear Equation Application with One Variable - Number Problem
This video provides and example of how to solve a number problem using a linear equation with one variable. One number is a multiple of the other. The difference is a constant. Find the two numbers. Library: http://mathispower4u.com Search: http://mathispower4u.wordpress.com
From playlist Whole Number Applications

Ex: Determine a Number that is Less Than and Greater than Using a Specific Place Value
This video provides examples of how to find a number that is less than and greater than a given number using a specific place value. Search Video Library at http://www.mathispower4u.wordpress.com
From playlist Whole Numbers: Place Value and Writing Numbers
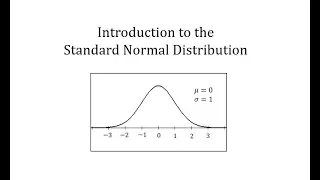
Introduction to the Standard Normal Distribution
This video introduces the standard normal distribution http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist The Normal Distribution
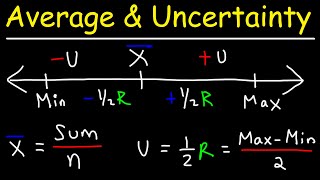
Averages and Uncertainty Calculations
This video tutorial explains how to calculate the average and uncertainty given a data set. The uncertainty is half of the range or half of the difference between the maximum and minimum values in the data set.
From playlist Statistics

Manfred Madritsch: Normal and Non-Normal Numbers
CIRM HYBRID EVENT Recorded during the meeting " Diophantine Problems, Determinism and Randomness" the February 04, 2021 by the Centre International de Rencontres Mathématiques (Marseille, France) Filmmaker: Guillaume Hennenfent Find this video and other talks given by worldwide mathem
From playlist Probability and Statistics

Verónica Becher: Independence of normal words
Abstract : Recall that normality is a elementary form of randomness: an infinite word is normal to a given alphabet if all blocks of symbols of the same length occur in the word with the same asymptotic frequency. We consider a notion of independence on pairs of infinite words formalising
From playlist Logic and Foundations

Letting Go Of Your Numbers Dependency
I teach physics. Trust me when I say that you need to learn to let go of your numbers dependency. In this video, I show why. Want Lecture Notes? http://www.flippingphysics.com/numbers-dependency.html Content Times: 0:00 Intro 0:43 Numbers Dependent Solution 4:26 Numbers Independent Soluti
From playlist JEE Physics Unit 3 - Laws of Motion and NEET Unit III - Laws of Motion

Distinguished Visitor Lecture Series Finding better randomness Theodore A. Slaman University of California, Berkeley, USA
From playlist Distinguished Visitors Lecture Series

Lecture 10 - Statistical Distributions
This is Lecture 10 of the CSE519 (Data Science) course taught by Professor Steven Skiena [http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~skiena/] at Stony Brook University in 2016. The lecture slides are available at: http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~skiena/519 More information may be found here: http://www
From playlist CSE519 - Data Science Fall 2016

Visual Group Thoery, Lecture 5.5: p-groups
Visual Group Thoery, Lecture 5.5: p-groups Before we can introduce the Sylow theorems, we need to develop some theory about groups of prime power order, which we call p-groups. In this lecture, we show that the number of fixed point of a p-group acting on a set S is congruent modulo p to
From playlist Visual Group Theory

PMSP - Random-like behavior in deterministic systems - Benjamin Weiss
Benjamin Weiss Einstein Institute of Math, Hebrew University June 16, 2010 For more videos, visit http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

Lec 5 | MIT 2.830J Control of Manufacturing Processes, S08
Lecture 5: Probability models, parameter estimation, and sampling Instructor: Duane Boning, David Hardt View the complete course at: http://ocw.mit.edu/2-830JS08 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT 2.830J, Control of Manufacturing Processes S08

Binary 6 – Normalised Floating Point Binary Fractions
This is the sixth in a series of videos about the binary number system which is fundamental to the operation of a digital electronic computer. In particular, this video covers the conversion of real numbers, both positive and negative, from denary into normalised floating point binary. It
From playlist Binary

Binary 7 – Floating Point Binary Addition
This is the seventh in a series of videos about the binary number system which is fundamental to the operation of a digital electronic computer. In particular, this video covers adding together floating point binary numbers for a given sized mantissa and exponent, both in two’s complement.
From playlist Binary

Normal Distribution: Find Probability Given Z-scores Using a Free Online Calculator
This video explains how to determine normal distribution probabilities given z-scores using a free online calculator. http://dlippman.imathas.com/graphcalc/graphcalc.html
From playlist The Normal Distribution