Continuous mappings | Calculus | Types of functions
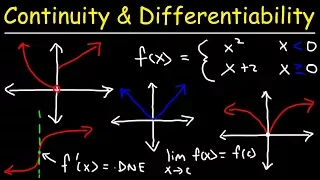
Continuous function
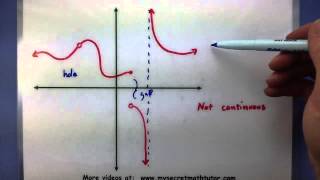
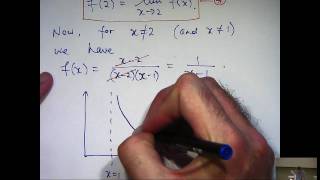
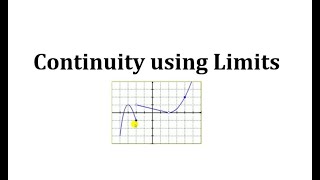
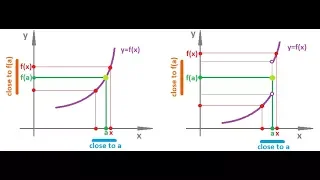
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function such that a continuous variation (that is a change without jump) of the argument induces a continuous variation of the value of the function. This means that there are no abrupt changes in value, known as discontinuities. More precisely, a function is continuous if arbitrarily small changes in its value can be assured by restricting to sufficiently small changes of its argument. A discontinuous function is a function that is not continuous. Up until the 19th century, mathematicians largely relied on intuitive notions of continuity, and considered only continuous functions. The epsilon–delta definition of a limit was introduced to formalize the definition of continuity. Continuity is one of the core concepts of calculus and mathematical analysis, where arguments and values of functions are real and complex numbers. The concept has been generalized to functions and . The latter are the most general continuous functions, and their definition is the basis of topology. A stronger form of continuity is uniform continuity. In order theory, especially in domain theory, a related concept of continuity is Scott continuity. As an example, the function H(t) denoting the height of a growing flower at time t would be considered continuous. In contrast, the function M(t) denoting the amount of money in a bank account at time t would be considered discontinuous, since it "jumps" at each point in time when money is deposited or withdrawn. (Wikipedia).