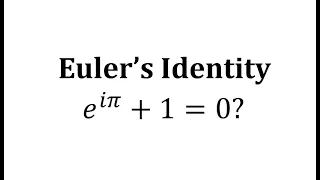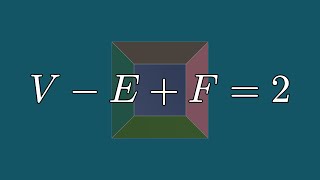Mental calculators | Mathematical analysts | Latin squares | Number theorists
Leonhard Euler
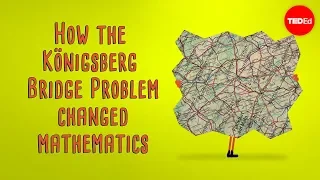
Leonhard Euler (/ˈɔɪlər/ OY-lər, German: [ˈɔʏlɐ]; 15 April 1707 – 18 September 1783) was a Swiss mathematician, physicist, astronomer, geographer, logician and engineer who founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made pioneering and influential discoveries in many other branches of mathematics such as analytic number theory, complex analysis, and infinitesimal calculus. He introduced much of modern mathematical terminology and notation, including the notion of a mathematical function. He is also known for his work in mechanics, fluid dynamics, optics, astronomy and music theory. Euler is held to be one of the greatest mathematicians in history and the greatest of the 18th century. A statement attributed to Pierre-Simon Laplace expresses Euler's influence on mathematics: "Read Euler, read Euler, he is the master of us all." Carl Friedrich Gauss remarked: "The study of Euler's works will remain the best school for the different fields of mathematics, and nothing else can replace it." Euler is also widely considered to be the most prolific; his 866 publications as well as his correspondences are collected in the Opera Omnia Leonhard Euler which, when completed, will consist of 81 quarto volumes. He spent most of his adult life in Saint Petersburg, Russia, and in Berlin, then the capital of Prussia. Euler is credited for popularizing the Greek letter (lowercase pi) to denote the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, as well as first using the notation for the value of a function, the letter to express the imaginary unit , the Greek letter (capital sigma) to express summations, the Greek letter (uppercase delta) for finite differences, and lowercase letters to represent the sides of a triangle while representing the angles as capital letters. He gave the current definition of the constant , the base of the natural logarithm, now known as Euler's number. Euler was also the first practitioner of graph theory (partly as a solution for the problem of the Seven Bridges of Königsberg). He became famous for, among many other accomplishments, solving the Basel problem, after proving that the sum of the infinite series of squared integer reciprocals equaled exactly π2/6, and for discovering that the sum of the numbers of vertices and faces minus edges of a polyhedron equals 2, a number now commonly known as the Euler characteristic. In the field of physics, Euler reformulated Newton's laws of physics into new laws in his two-volume work Mechanica to better explain the motion of rigid bodies. He also made substantial contributions to the study of elastic deformations of solid objects. (Wikipedia).