Real analysis | Complex analysis | Series expansions
Taylor series
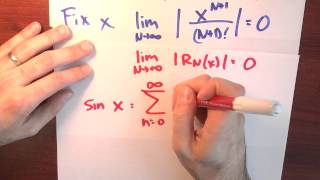
In mathematics, the Taylor series or Taylor expansion of a function is an infinite sum of terms that are expressed in terms of the function's derivatives at a single point. For most common functions, the function and the sum of its Taylor series are equal near this point. Taylor series are named after Brook Taylor, who introduced them in 1715. A Taylor series is also called a Maclaurin series, when 0 is the point where the derivatives are considered, after Colin Maclaurin, who made extensive use of this special case of Taylor series in the mid-18th century. The partial sum formed by the first n + 1 terms of a Taylor series is a polynomial of degree n that is called the nth Taylor polynomial of the function. Taylor polynomials are approximations of a function, which become generally better as n increases. Taylor's theorem gives quantitative estimates on the error introduced by the use of such approximations. If the Taylor series of a function is convergent, its sum is the limit of the infinite sequence of the Taylor polynomials. A function may differ from the sum of its Taylor series, even if its Taylor series is convergent. A function is analytic at a point x if it is equal to the sum of its Taylor series in some open interval (or open disk in the complex plane) containing x. This implies that the function is analytic at every point of the interval (or disk). (Wikipedia).