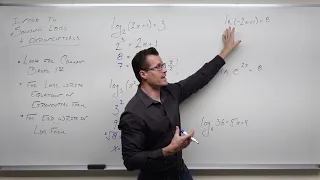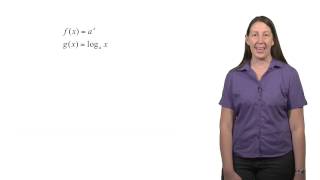Unary operations | Exponentials
Exponentiation
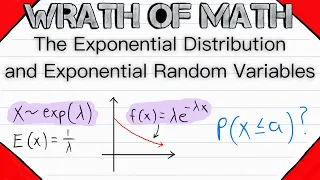
Exponentiation is a mathematical operation, written as bn, involving two numbers, the base b and the exponent or power n, and pronounced as "b (raised) to the (power of) n". When n is a positive integer, exponentiation corresponds to repeated multiplication of the base: that is, bn is the product of multiplying n bases: The exponent is usually shown as a superscript to the right of the base. In that case, bn is called "b raised to the nth power", "b (raised) to the power of n", "the nth power of b", "b to the nth power", or most briefly as "b to the nth". Starting from the basic fact stated above that, for any positive integer , is occurrences of all multiplied by each other, several other properties of exponentiation directly follow. In particular: In other words, when multiplying a base raised to one exponent by the same base raised to another exponent, the exponents add. From this basic rule that exponents add, we can derive that must be equal to 1, as follows. For any , . Dividing both sides by gives . The fact that can similarly be derived from the same rule. For example, . Taking the cube root of both sides gives . The rule that multiplying makes exponents add can also be used to derive the properties of negative integer exponents. Consider the question of what should mean. In order to respect the "exponents add" rule, it must be the case that . Dividing both sides by gives , which can be more simply written as , using the result from above that . By a similar argument, . The properties of fractional exponents also follow from the same rule. For example, suppose we consider and ask if there is some suitable exponent, which we may call , such that . From the definition of the square root, we have that . Therefore, the exponent must be such that . Using the fact that multiplying makes exponents add gives . The on the right-hand side can also be written as , giving . Equating the exponents on both sides, we have . Therefore, , so . The definition of exponentiation can be extended to allow any real or complex exponent. Exponentiation by integer exponents can also be defined for a wide variety of algebraic structures, including matrices. Exponentiation is used extensively in many fields, including economics, biology, chemistry, physics, and computer science, with applications such as compound interest, population growth, chemical reaction kinetics, wave behavior, and public-key cryptography. (Wikipedia).