
Algebraic Structures: Groups, Rings, and Fields
This video covers the definitions for some basic algebraic structures, including groups and rings. I give examples of each and discuss how to verify the properties for each type of structure.
From playlist Abstract Algebra

Sets and other data structures | Data Structures in Mathematics Math Foundations 151
In mathematics we often want to organize objects. Sets are not the only way of doing this: there are other data types that are also useful and that can be considered together with set theory. In particular when we group objects together, there are two fundamental questions that naturally a
From playlist Math Foundations
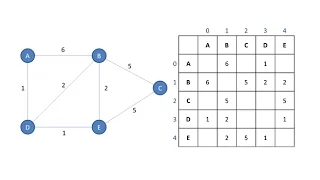
Graph Data Structure 1. Terminology and Representation (algorithms)
This is the first in a series of videos about the graph data structure. It mentions the applications of graphs, defines various terminology associated with graphs, and describes how a graph can be represented programmatically by means of adjacency lists or an adjacency matrix.
From playlist Data Structures

Data structures: Introduction to Trees
See complete series on data structures here: http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL2_aWCzGMAwI3W_JlcBbtYTwiQSsOTa6P In this lesson, we have described tree data structure as a logical model in computer science. We have briefly discussed tree as a non-linear hierarchical data structure, i
From playlist Data structures

Data structures: Introduction to graphs
See complete series on data structures here: http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL2_aWCzGMAwI3W_JlcBbtYTwiQSsOTa6P In this lesson, we have described Graph data structure as a mathematical model. We have briefly described the concept of Graph and some of its applications. For practice
From playlist Data structures
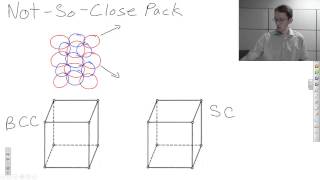
Not-So-Close Packed Crystal Structures
A description of two crystal structures that are created from not-so-close packed structures.
From playlist Atomic Structures and Bonding
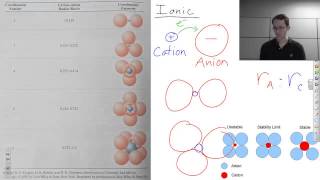
Ceramic Crystal Structure Geometry
A description of how different bonding causes different geometries in ceramic crystal structures.
From playlist Atomic Structures and Bonding
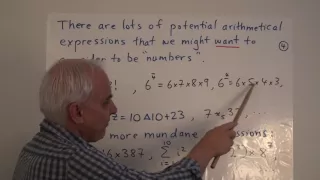
Arithmetical expressions as natural numbers | Data structures in Mathematics Math Foundations 194
Primitive natural numbers and Hindu Arabic numerals can be pinned down very concretely and precisely. But what about numbers expressed via more elaborate arithmetical expressions, perhaps involving towers of exponents, or hyperoperations? Is there a consistent and logical proper way of set
From playlist Math Foundations

Max Tegmark - Is Mathematics Invented or Discovered?
Free access Closer to Truth's library of 5,000 videos: http://bit.ly/2UufzC7 Mathematics describes the real world of atoms and acorns, stars and stairs, with remarkable precision. So is mathematics invented by humans just like chisels and hammers and pieces of music? Or is mathematics dis
From playlist Closer To Truth - Max Tegmark Interviews

Max Tegmark - What is Ultimate Reality?
What is the deepest nature of things? Our world is complex, filled with so much stuff. But down below, what's most fundamental, what is ultimate reality? Is there anything nonphysical? Anything spiritual? Or only the physical world? Many feel certain of their belief, on each side of contro
From playlist Closer To Truth - Max Tegmark Interviews

Stanford Seminar - On the Origin of Experience: The Shaping of Sense and the Complex World
"On the Origin of Experience: The Shaping of Sense and the Complex World" -Steven Ericsson-Zenith Colloquium on Computer Systems Seminar Series (EE380) presents the current research in design, implementation, analysis, and use of computer systems. Topics range from integrated circuits to
From playlist Engineering

Max Tegmark - Is Mathematics Eternal?
Mathematics is like nothing else. The truths of math seem to be unrelated to anything else—independent of human beings, independent of the universe. The sum of 2 + 3 = 5 cannot be untrue; this means that 2 + 3 = 5 would be true even if there were never any human beings, even if there were
From playlist Closer To Truth - Max Tegmark Interviews

Oxford Mathematics Public Lectures: James Sparks and City of London Sinfonia - Bach and the Cosmos Johann Sebastian Bach was the most mathematical of composers. Oxford Mathematician and Cambridge organ scholar James Sparks will explain just how mathematical and City of London Sinfonia wil
From playlist Music and Mathematics

Isomorphic Structures of any Kind are `Equal' in HoTT: But What... Structure? - Peter Aczel
Peter Aczel The Unviersity of Manchester; Member,School of Mathematics February 7, 2013 For more videos, visit http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

Fun with lists, multisets and sets III | Data Structures in Mathematics Math Foundations 154
We continue our discussion of data structures in mathematics, now treating the case of multisets or msets. This is an unordered structure in which repetitions are allowed. It turns out that multisets support interesting algebraic structures: notable we are able to add two multisets to get
From playlist Math Foundations

Max Tegmark - Why There is "Something" rather than "Nothing"
We know that there is not Nothing. There is Something. It is not the case that there is no world, nothing at all, a blank. It is the case that there is a world. Nothing did not obtain. But why? Click here to watch more interviews on the reason there is something rather than nothing http:/
From playlist Closer To Truth - Max Tegmark Interviews

Исследование наноструктур методом сильной связи в системе Mathematica
Василий Сороко Норвежский университет естественных и технических наук
From playlist Russian Virtual Conference 2019

Atomistically inspired origami
Oxford Mathematics Public Lectures - Richard James - Atomistically inspired origami The World population is growing at about 80 million per year. As time goes by, there is necessarily less space per person. Perhaps this is why the scientific community seems to be obsessed with folding t
From playlist Oxford Mathematics Public Lectures

SHM - 16/01/15 - Constructivismes en mathématiques - Thierry Coquand
Thierry Coquand (Université de Gothenburg), « Théorie des types et mathématiques constructives »
From playlist Les constructivismes mathématiques - Séminaire d'Histoire des Mathématiques

What is the definition of a geometric sequence
👉 Learn about sequences. A sequence is a list of numbers/values exhibiting a defined pattern. A number/value in a sequence is called a term of the sequence. There are many types of sequence, among which are: arithmetic and geometric sequence. An arithmetic sequence is a sequence in which
From playlist Sequences