
Introduction to Direct Proofs: If n is even, then n squared is even
This video introduces the mathematical proof method of direct proof provides an example of a direct proof. mathispower4u.com
From playlist Symbolic Logic and Proofs (Discrete Math)

Introduction to Common Mathematical Proof Methods
This video introduces the common methods of mathematical proofs and provides a basic example of a direct proof. mathispower4u.com
From playlist Symbolic Logic and Proofs (Discrete Math)

Basic Methods: We note the different methods of informal proof, which include direct proof, proof by contradiction, and proof by induction. We give proofs that sqrt(2) is irrational and that there are infinitely many primes, among others.
From playlist Math Major Basics

SImple proofs and their variations -- Proofs
This lecture is on Introduction to Higher Mathematics (Proofs). For more see http://calculus123.com.
From playlist Proofs
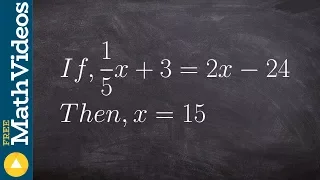
Learn how to write an algebraic proof
👉 Learn how to write an algebraic proof. Algebraic proofs are used to help students understand how to write formal proofs where we have a statement and a reason. In the case of an algebraic proof the statement will be the operations used to solve an algebraic equation and the reason will
From playlist Parallel Lines and a Transversal
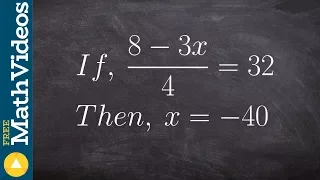
Learning to write an algebraic proof
👉 Learn how to write an algebraic proof. Algebraic proofs are used to help students understand how to write formal proofs where we have a statement and a reason. In the case of an algebraic proof the statement will be the operations used to solve an algebraic equation and the reason will
From playlist Parallel Lines and a Transversal
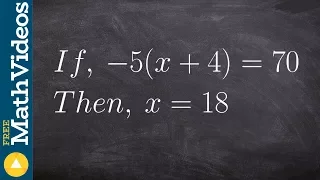
How to write an algebraic proof
👉 Learn how to write an algebraic proof. Algebraic proofs are used to help students understand how to write formal proofs where we have a statement and a reason. In the case of an algebraic proof the statement will be the operations used to solve an algebraic equation and the reason will
From playlist Parallel Lines and a Transversal

Basic Methods: We define theorems and describe how to formally construct a proof. We note further rules of inference and show how the logical equivalence of reductio ad absurdum allows proof by contradiction.
From playlist Math Major Basics

Séminaire Bourbaki - 21/06/2014 - 3/4 - Thomas C. HALES
Developments in formal proofs A for mal proof is a proof that can be read and verified by computer, directly from the fundamental rules of logic and the foundational axioms of mathematics. The technology behind for mal proofs has been under development for decades and grew out of efforts i
From playlist Bourbaki - 21 juin 2014

8ECM Invited Lecture: Andrej Bauer
From playlist 8ECM Invited Lectures

Fabian Immler, Carnegie Mellon University Formal mathematics and a proof of chaos Formal proof has been successfully applied to the verification of hardware and software systems. But formal proof is also applicable to mathematics: proofs can be checked with ultimate rigor and one can bui
From playlist Fall 2019 Kolchin Seminar in Differential Algebra

Tony Wu - Autoformalization with Large Language Models - IPAM at UCLA
Recorded 15 February 2023. Tony Wu of Google presents "Autoformalization with Large Language Models" at IPAM's Machine Assisted Proofs Workshop. Abstract: Autoformalization is the process of automatically translating from natural language mathematics to formal specifications and proofs. A
From playlist 2023 Machine Assisted Proofs Workshop

Heather Macbeth - Algorithm and abstraction in formal mathematics - IPAM at UCLA
Recorded 17 February 2023. Heather Macbeth of Fordham University at Lincoln Center presents "Algorithm and abstraction in formal mathematics" at IPAM's Machine Assisted Proofs Workshop. Abstract: Paradoxically, the formalized version of a proof is often both more abstract and more computat
From playlist 2023 Machine Assisted Proofs Workshop

3 - Kick-off afternoon : Thomas Hales, Formalizing the proof of the Kepler Conjecture
Thomas Hales (University of Pittsburgh): Formalizing the proof of the Kepler Conjecture
From playlist T2-2014 : Semantics of proofs and certified mathematics

First Author Interview: AI & formal math (Formal Mathematics Statement Curriculum Learning)
#openai #math #imo This is an interview with Stanislas Polu, research engineer at OpenAI and first author of the paper "Formal Mathematics Statement Curriculum Learning". Watch the paper review here: https://youtu.be/lvYVuOmUVs8 OUTLINE: 0:00 - Intro 2:00 - How do you explain the big pub
From playlist Applications of ML

Foundations of Mathematics and Homotopy Theory - Vladimir Voevodsky
Vladimir Voevodsky Institute for Advanced Study March 22, 2006 More videos on http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

What if Current Foundations of Mathematics are Inconsistent? | Vladimir Voevodsky
Vladimir Voevodsky, Professor, School of Mathematics, Institute for Advanced Study http://www.ias.edu/people/faculty-and-emeriti/voevodsky In this lecture, Professor Vladimir Voevodsky begins with Gödel's second incompleteness theorem to discuss the possibility that the formal theory of f
From playlist Mathematics

Micaela Mayero - Overview of real numbers in theorem provers: application with real analysis in Coq
Recorded 15 February 2023. Micaela Mayero of the Galilee Institute - Paris Nord University presents "An overview of the real numbers in theorem provers: an application with real analysis in Coq" at IPAM's Machine Assisted Proofs Workshop. Abstract: Formalizing real numbers in a formal proo
From playlist 2023 Machine Assisted Proofs Workshop

Proof: What is it, and how does it work?
From playlist The Nature of Proof
