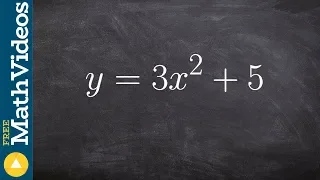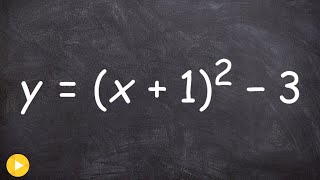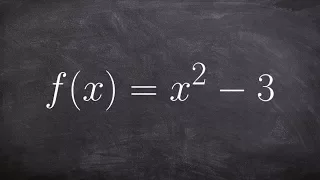Unary operations | Multiplication | Abstract algebra | Elementary algebra | Elementary special functions
Multiplicative inverse
In mathematics, a multiplicative inverse or reciprocal for a number x, denoted by 1/x or x−1, is a number which when multiplied by x yields the multiplicative identity, 1. The multiplicative inverse of a fraction a/b is b/a. For the multiplicative inverse of a real number, divide 1 by the number. For example, the reciprocal of 5 is one fifth (1/5 or 0.2), and the reciprocal of 0.25 is 1 divided by 0.25, or 4. The reciprocal function, the function f(x) that maps x to 1/x, is one of the simplest examples of a function which is its own inverse (an involution). Multiplying by a number is the same as dividing by its reciprocal and vice versa. For example, multiplication by 4/5 (or 0.8) will give the same result as division by 5/4 (or 1.25). Therefore, multiplication by a number followed by multiplication by its reciprocal yields the original number (since the product of the number and its reciprocal is 1). The term reciprocal was in common use at least as far back as the third edition of Encyclopædia Britannica (1797) to describe two numbers whose product is 1; geometrical quantities in inverse proportion are described as reciprocall in a 1570 translation of Euclid's Elements. In the phrase multiplicative inverse, the qualifier multiplicative is often omitted and then tacitly understood (in contrast to the additive inverse). Multiplicative inverses can be defined over many mathematical domains as well as numbers. In these cases it can happen that ab ≠ ba; then "inverse" typically implies that an element is both a left and right inverse. The notation f −1 is sometimes also used for the inverse function of the function f, which is for most functions not equal to the multiplicative inverse. For example, the multiplicative inverse 1/(sin x) = (sin x)−1 is the cosecant of x, and not the inverse sine of x denoted by sin−1 x or arcsin x. The terminology difference reciprocal versus inverse is not sufficient to make this distinction, since many authors prefer the opposite naming convention, probably for historical reasons (for example in French, the inverse function is preferably called the bijection réciproque). (Wikipedia).