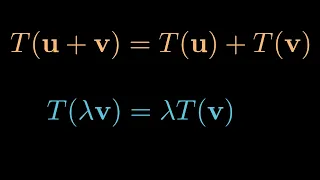Transformation (function) | Abstract algebra | Linear operators | Functions and mappings
Linear map
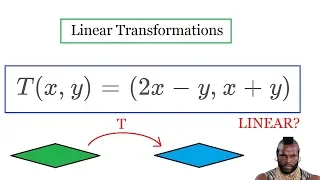
In mathematics, and more specifically in linear algebra, a linear map (also called a linear mapping, linear transformation, vector space homomorphism, or in some contexts linear function) is a mapping between two vector spaces that preserves the operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication. The same names and the same definition are also used for the more general case of modules over a ring; see Module homomorphism. If a linear map is a bijection then it is called a linear isomorphism. In the case where , a linear map is called a (linear) endomorphism. Sometimes the term linear operator refers to this case, but the term "linear operator" can have different meanings for different conventions: for example, it can be used to emphasize that and are real vector spaces (not necessarily with ), or it can be used to emphasize that is a function space, which is a common convention in functional analysis. Sometimes the term linear function has the same meaning as linear map, while in analysis it does not. A linear map from V to W always maps the origin of V to the origin of W. Moreover, it maps linear subspaces in V onto linear subspaces in W (possibly of a lower dimension); for example, it maps a plane through the origin in V to either a plane through the origin in W, a line through the origin in W, or just the origin in W. Linear maps can often be represented as matrices, and simple examples include rotation and reflection linear transformations. In the language of category theory, linear maps are the morphisms of vector spaces. (Wikipedia).