
Statistics: Introduction (1 of 13) Listing of Topics Covered
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! We will review Introduction chapter the topics that will list the topics/chapters that will be covered in Statistics: Introduction, Graphical Representation of Data, Bivariate Data and Linear Regression, Probability, Prob
From playlist STATISTICS CH 1 INTRODUCTION

(PP 6.1) Multivariate Gaussian - definition
Introduction to the multivariate Gaussian (or multivariate Normal) distribution.
From playlist Probability Theory

Statistics Lecture 5.2: A Study of Probability Distributions, Mean, and Standard Deviation
https://www.patreon.com/ProfessorLeonard Statistics Lecture 5.2: A Study of Probability Distributions, Mean, and Standard Deviation
From playlist Statistics (Full Length Videos)

(PP 6.2) Multivariate Gaussian - examples and independence
Degenerate multivariate Gaussians. Some sketches of examples and non-examples of Gaussians. The components of a Gaussian are independent if and only if they are uncorrelated.
From playlist Probability Theory

Statistics Lecture 5.2 Part 1: Probability Distributions, Mean, and Standard Deviation
From playlist Statistics Playlist 1
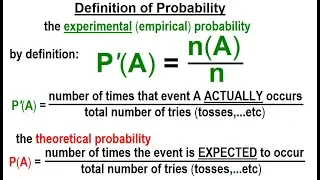
Statistics: Ch 4 Probability in Statistics (20 of 74) Definition of Probability
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! To donate: http://www.ilectureonline.com/donate https://www.patreon.com/user?u=3236071 We will learn the “strict” definition of experimental (empirical) and theoretical probability. Next video in this series can be seen
From playlist STATISTICS CH 4 STATISTICS IN PROBABILITY

Statistics Lecture 4.2 Part 4: Introduction to Probability
From playlist Statistics Playlist 1

Statistics Lecture 5.2 Part 2: Probability Distributions, Mean, and Standard Deviation
From playlist Statistics Playlist 1

Statistics Lecture 4.2 Part 1: Introduction to Probability
From playlist Statistics Playlist 1

Summary of joint vs unconditional vs conditional probability (FRM T2-3a)
This is just a briefer summary of the three probability terms reviewed in the previous video. Conditional equals joint divided by unconditional probability. Discuss this video here in our FRM forum: https://trtl.bz/2Az187d Subscribe here https://www.youtube.com/c/bionicturtle?sub-confirma
From playlist Quantitative Analysis (FRM Topic 2)

[Here is my XLS https://www.dropbox.com/s/thqkesz65niutil/1204-yt-probability-matrix.xlsx] The probability matrix includes joint probabilities on the "inside" and unconditional (aka, marginal) probabilities on the outside. The key relationship is joint probability = unconditional * conditi
From playlist Quantitative Analysis (FRM Topic 2)

Bayes Theorem, Three-state variable (FRM T2-9c)
[https://trtl.bz/220122-bayes-three-states] This explores the answer to Miller's sample question in Chapter 6 of http://amzn.to/2C88m0i. There are three types of managers: Out-performers (MO), in-line performers (MI) and under-performers (MU). The prior probability that a manager is an out
From playlist Quantitative Analysis (FRM Topic 2)

What is statistical independence? (FRM T2-4)
[Here is my XLS http://trtl.bz/2kucVOv] Variables are independent if and only if (iff) their JOINT probability is equal to the product of their unconditional (aka, marginal) probabilities; i.e., if and only if Prob(X,Y) = Prob(X)*Prob(Y). Further, if variables are independent then their co
From playlist Quantitative Analysis (FRM Topic 2)

Bayes Theorem: Simple test for disease (FRM T2-9)
[my xls is here http://trtl.bz/2BO9LNq] Bayes Theorem updates a conditional probability with new evidence. In this case, the conditional probability (disease | positive test result) equals the joint probability (disease, positive test result) divided by the unconditional probability (posit
From playlist Quantitative Analysis (FRM Topic 2)
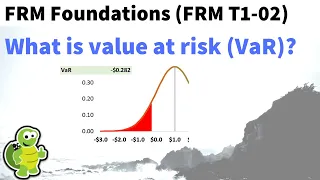
What is value at risk (VaR)? FRM T1-02
Value at risk is just a statistical feature of the probability distribution (the hard part is specifying the probability distribution): VaR is the quantile associated with a selected probability; i.e., what's the worst that can happen with some level of confidence? (Here is my XLS http://t
From playlist Risk Foundations (FRM Topic 1)

AQA Advance Information GCSE Maths | Foundation| Paper 2 | 7th June 2022
AQA Advance Information GCSE Maths - Every topic in the AQA GCSE Maths Foundaion Tier Paper 2 on June 7th 2022. I provide example questions for each topic, along with additional revision resources to help you prepare for this exam! EXAMPLE QUESTIONS Follow each link to go straight to an
From playlist GCSE Maths Advance Information - All Summary Videos

Bayes Theorem, adding a bit of complexity (FRM T2- 9b)
[Here is my XLS at http://trtl.bz/122717-YT-Bayes-2nd-Star-Mgr] and Here is the question: "You are an analyst at Astra Fund of Funds. Based on an examination of historical data, you determine that all fund managers fall into one of two groups. Stars are the best managers. The probability t
From playlist Quantitative Analysis (FRM Topic 2)

Probability functions: pdf, CDF and inverse CDF (FRM T2-1)
[Here is my XLS @ http://trtl.bz/2AgvfRo] A function is a viable probability function if it has a valid CDF (i.e., is bounded by zero and one) which is the integral of the probability density function (pdf). The inverse CDF (aka, quantile function) returns the quantile associated with a pr
From playlist Quantitative Analysis (FRM Topic 2)

Live CEOing Ep 257: Language Design in Wolfram Language
Watch Stephen Wolfram and teams of developers in a live, working, language design meeting. This episode is about Language Design in the Wolfram Language.
From playlist Behind the Scenes in Real-Life Software Design
Statistics Lecture 6.2: Introduction to the Normal Distribution and Continuous Random Variables
https://www.patreon.com/ProfessorLeonard Statistics Lecture 6.2: Introduction to the Normal Distribution and Continuous Random Variables
From playlist Statistics (Full Length Videos)