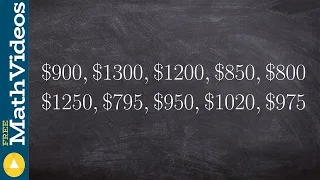Summary statistics | Statistical deviation and dispersion
Standard deviation
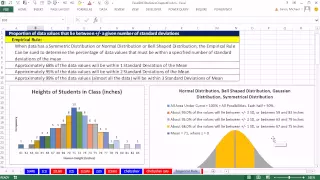
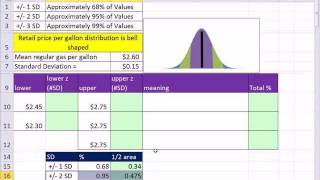
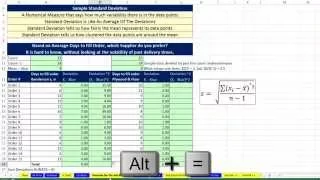
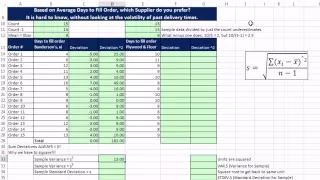
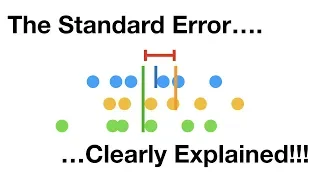
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD, and is most commonly represented in mathematical texts and equations by the lower case Greek letter σ (sigma), for the population standard deviation, or the Latin letter s, for the sample standard deviation. The standard deviation of a random variable, sample, statistical population, data set, or probability distribution is the square root of its variance. It is algebraically simpler, though in practice less robust, than the average absolute deviation. A useful property of the standard deviation is that, unlike the variance, it is expressed in the same unit as the data. The standard deviation of a population or sample and the standard error of a statistic (e.g., of the sample mean) are quite different, but related. The sample mean's standard error is the standard deviation of the set of means that would be found by drawing an infinite number of repeated samples from the population and computing a mean for each sample. The mean's standard error turns out to equal the population standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size, and is estimated by using the sample standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size. For example, a poll's standard error (what is reported as the margin of error of the poll), is the expected standard deviation of the estimated mean if the same poll were to be conducted multiple times. Thus, the standard error estimates the standard deviation of an estimate, which itself measures how much the estimate depends on the particular sample that was taken from the population. In science, it is common to report both the standard deviation of the data (as a summary statistic) and the standard error of the estimate (as a measure of potential error in the findings). By convention, only effects more than two standard errors away from a null expectation are considered "statistically significant", a safeguard against spurious conclusion that is really due to random sampling error. When only a sample of data from a population is available, the term standard deviation of the sample or sample standard deviation can refer to either the above-mentioned quantity as applied to those data, or to a modified quantity that is an unbiased estimate of the population standard deviation (the standard deviation of the entire population). (Wikipedia).