Moment (mathematics) | Articles containing proofs | Statistical deviation and dispersion
Variance
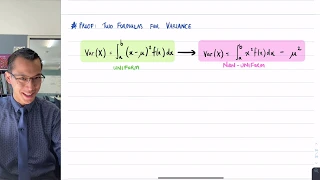
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expectation of the squared deviation of a random variable from its population mean or sample mean. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. Variance has a central role in statistics, where some ideas that use it include descriptive statistics, statistical inference, hypothesis testing, goodness of fit, and Monte Carlo sampling. Variance is an important tool in the sciences, where statistical analysis of data is common. The variance is the square of the standard deviation, the second central moment of a distribution, and the covariance of the random variable with itself, and it is often represented by , , , , or . An advantage of variance as a measure of dispersion is that it is more amenable to algebraic manipulation than other measures of dispersion such as the expected absolute deviation; for example, the variance of a sum of uncorrelated random variables is equal to the sum of their variances. A disadvantage of the variance for practical applications is that, unlike the standard deviation, its units differ from the random variable, which is why the standard deviation is more commonly reported as a measure of dispersion once the calculation is finished. There are two distinct concepts that are both called "variance". One, as discussed above, is part of a theoretical probability distribution and is defined by an equation. The other variance is a characteristic of a set of observations. When variance is calculated from observations, those observations are typically measured from a real world system. If all possible observations of the system are present then the calculated variance is called the population variance. Normally, however, only a subset is available, and the variance calculated from this is called the sample variance. The variance calculated from a sample is considered an estimate of the full population variance. There are multiple ways to calculate an estimate of the population variance, as discussed in the section below. The two kinds of variance are closely related. To see how, consider that a theoretical probability distribution can be used as a generator of hypothetical observations. If an infinite number of observations are generated using a distribution, then the sample variance calculated from that infinite set will match the value calculated using the distribution's equation for variance. (Wikipedia).