Articles containing proofs | Probability theorems | Central limit theorem | Asymptotic theory (statistics) | Theorems in statistics
Central limit theorem
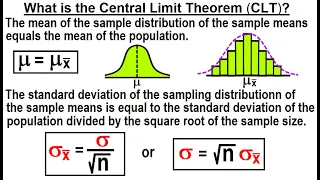
In probability theory, the central limit theorem (CLT) establishes that, in many situations, when independent random variables are summed up, their properly normalized sum tends toward a normal distribution even if the original variables themselves are not normally distributed. The theorem is a key concept in probability theory because it implies that probabilistic and statistical methods that work for normal distributions can be applicable to many problems involving other types of distributions. This theorem has seen many changes during the formal development of probability theory. Previous versions of the theorem date back to 1811, but in its modern general form, this fundamental result in probability theory was precisely stated as late as 1920, thereby serving as a bridge between classical and modern probability theory. If are random samples drawn from a population with overall mean and finite variance , and if is the sample mean of the first samples, then the limiting form of the distribution, , with , is a standard normal distribution. For example, suppose that a sample is obtained containing many observations, each observation being randomly generated in a way that does not depend on the values of the other observations, and that the arithmetic mean of the observed values is computed. If this procedure is performed many times, the central limit theorem says that the probability distribution of the average will closely approximate a normal distribution. The central limit theorem has several variants. In its common form, the random variables must be independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.). In variants, convergence of the mean to the normal distribution also occurs for non-identical distributions or for non-independent observations, if they comply with certain conditions. The earliest version of this theorem, that the normal distribution may be used as an approximation to the binomial distribution, is the de Moivre–Laplace theorem. (Wikipedia).