Convergence (mathematics) | Stochastic processes
Convergence of random variables
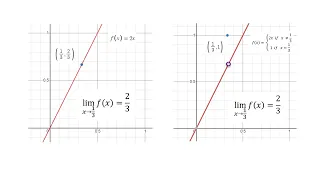
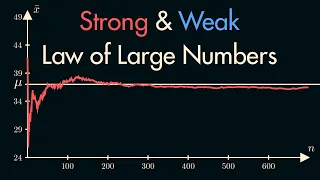
In probability theory, there exist several different notions of convergence of random variables. The convergence of sequences of random variables to some limit random variable is an important concept in probability theory, and its applications to statistics and stochastic processes. The same concepts are known in more general mathematics as stochastic convergence and they formalize the idea that a sequence of essentially random or unpredictable events can sometimes be expected to settle down into a behavior that is essentially unchanging when items far enough into the sequence are studied. The different possible notions of convergence relate to how such a behavior can be characterized: two readily understood behaviors are that the sequence eventually takes a constant value, and that values in the sequence continue to change but can be described by an unchanging probability distribution. (Wikipedia).
.gif?width=300)