Branching process
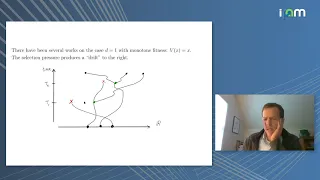
In probability theory, a branching process is a type of mathematical object known as a stochastic process, which consists of collections of random variables. The random variables of a stochastic process are indexed by the natural numbers. The original purpose of branching processes was to serve as a mathematical model of a population in which each individual in generation produces some random number of individuals in generation , according, in the simplest case, to a fixed probability distribution that does not vary from individual to individual. Branching processes are used to model reproduction; for example, the individuals might correspond to bacteria, each of which generates 0, 1, or 2 offspring with some probability in a single time unit. Branching processes can also be used to model other systems with similar dynamics, e.g., the spread of surnames in genealogy or the propagation of neutrons in a nuclear reactor. A central question in the theory of branching processes is the probability of ultimate extinction, where no individuals exist after some finite number of generations. Using Wald's equation, it can be shown that starting with one individual in generation zero, the expected size of generation n equals μn where μ is the expected number of children of each individual. If μ < 1, then the expected number of individuals goes rapidly to zero, which implies ultimate extinction with probability 1 by Markov's inequality. Alternatively, if μ > 1, then the probability of ultimate extinction is less than 1 (but not necessarily zero; consider a process where each individual either has 0 or 100 children with equal probability. In that case, μ = 50, but probability of ultimate extinction is greater than 0.5, since that's the probability that the first individual has 0 children). If μ = 1, then ultimate extinction occurs with probability 1 unless each individual always has exactly one child. In theoretical ecology, the parameter μ of a branching process is called the basic reproductive rate. (Wikipedia).