Polyhedron
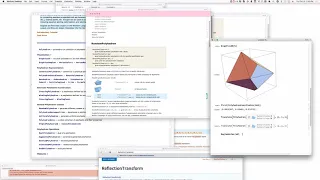
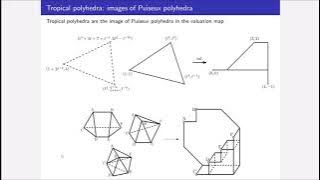
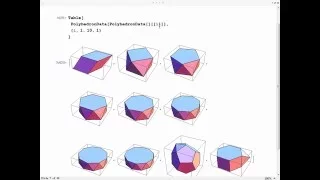
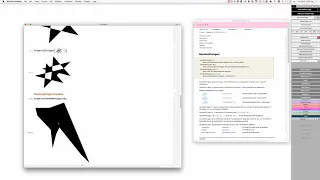
In geometry, a polyhedron (plural polyhedra or polyhedrons; from Greek πολύ (poly-) 'many', and εδρον (-hedron) 'base, seat') is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices. A convex polyhedron is the convex hull of finitely many points, not all on the same plane. Cubes and pyramids are examples of convex polyhedra. A polyhedron is a 3-dimensional example of a polytope, a more general concept in any number of dimensions. (Wikipedia).