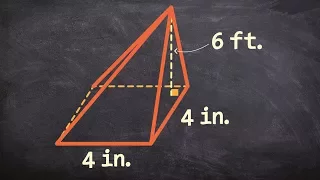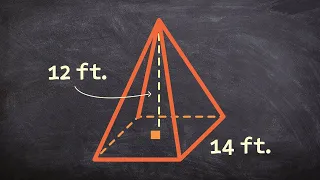Self-dual polyhedra | Geometric shapes | Polyhedra | Prismatoid polyhedra | Pyramids and bipyramids
Pyramid (geometry)
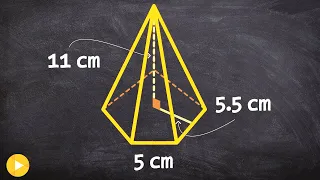
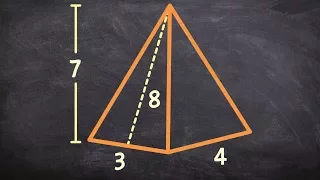
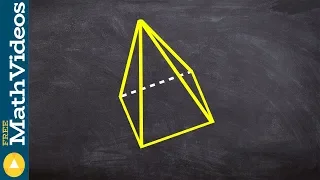
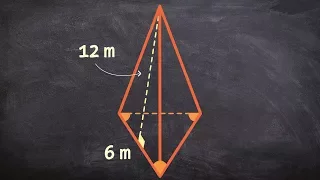
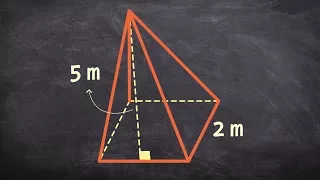
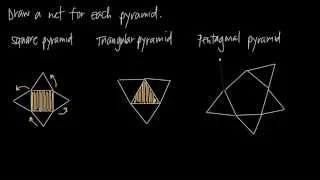
In geometry, a pyramid (from Greek πυραμίς (pyramís)) is a polyhedron formed by connecting a polygonal base and a point, called the apex. Each base edge and apex form a triangle, called a lateral face. It is a conic solid with polygonal base. A pyramid with an n-sided base has n + 1 vertices, n + 1 faces, and 2n edges. All pyramids are self-dual. A right pyramid has its apex directly above the centroid of its base. Nonright pyramids are called oblique pyramids. A regular pyramid has a regular polygon base and is usually implied to be a right pyramid. When unspecified, a pyramid is usually assumed to be a regular square pyramid, like the physical pyramid structures. A triangle-based pyramid is more often called a tetrahedron. Among oblique pyramids, like acute and obtuse triangles, a pyramid can be called acute if its apex is above the interior of the base and obtuse if its apex is above the exterior of the base. A right-angled pyramid has its apex above an edge or vertex of the base. In a tetrahedron these qualifiers change based on which face is considered the base. Pyramids are a class of the prismatoids. Pyramids can be doubled into bipyramids by adding a second offset point on the other side of the base plane. (Wikipedia).