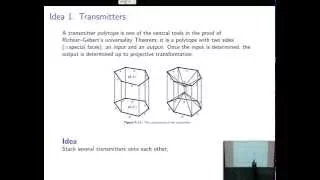
Polytopes | Real algebraic geometry
Polytope
In elementary geometry, a polytope is a geometric object with flat sides (faces). Polytopes are the generalization of three-dimensional polyhedra to any number of dimensions. Polytopes may exist in any general number of dimensions n as an n-dimensional polytope or n-polytope. For example, a two-dimensional polygon is a 2-polytope and a three-dimensional polyhedron is a 3-polytope. In this context, "flat sides" means that the sides of a (k + 1)-polytope consist of k-polytopes that may have (k – 1)-polytopes in common. Some theories further generalize the idea to include such objects as unbounded apeirotopes and tessellations, decompositions or tilings of curved manifolds including spherical polyhedra, and set-theoretic abstract polytopes. Polytopes of more than three dimensions were first discovered by Ludwig Schläfli before 1853, who called such a figure a polyschem. The German term polytop was coined by the mathematician Reinhold Hoppe, and was introduced to English mathematicians as polytope by Alicia Boole Stott. (Wikipedia).