
http://www.teachastronomy.com/ Hipparchus was a major astronomer of the second century BC. He had an observatory on the island of Rhodes. From him we have the first use of celestial coordinates and the first star catalog. He also invented the magnitude system for measuring the relative
From playlist 03. Concepts and History of Astronomy and Physics

Plato on Knowledge - The Meno & Theaetetus (History of Philosophy)
Peter Adamson discusses Plato's dialogues the Meno and the Theaetetus, which address various epistemological topics, including Meno's paradox, Plato's theory of recollection, the nature of knowledge, relativism, and the difference between knowledge and true belief (e.g. what must be added
From playlist Socrates & Plato

Subscribe to our YouTube Channel for all the latest from World Science U. Visit our Website: http://www.worldscienceu.com/ Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/worldscienceu Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/worldscienceu
From playlist Science Unplugged: Physics

If God Knows the Future, What is Free Will? | Episode 710 | Closer To Truth
If God is infallible and knows the future perfectly, then God knows what I will do at every moment from my birth to my death. So where's my free will? Featuring interviews with Alvin Plantinga, Peter van Inwagen, Thomas Flint, and Dean Zimmerman. Season 7, Episode 10 - #CloserToTruth ▶Re
From playlist Big Questions About God - Closer To Truth - Core Topic

Mechanics and curves | Math History | NJ Wildberger
The laws of motion as set out by Newton built upon work of Oresme, Galileo and others on dynamics, and the relations between distance, velocity and acceleration in trajectories. With Newton's laws and the calculus, a whole new arena of practical and theoretical investigations opened up to
From playlist MathHistory: A course in the History of Mathematics

Number theory and algebra in Asia (a) | Math History | NJ Wildberger
After the later Alexandrian mathematicians Ptolemy and Diophantus, Greek mathematics went into decline and the focus shifted eastward. This lecture discusses some aspects of Chinese, Indian and Arab mathematics, in particular the interest in number theory: Pell's equation, the Chinese rema
From playlist MathHistory: A course in the History of Mathematics

The Philosophy of Language - John Searle & Bryan Magee (1978)
In this program, John Searle discusses the philosophy of language with Bryan Magee. This is from a 1978 series on Modern Philosophy called Men of Ideas. #Philosophy #BryanMagee #Searle
From playlist Bryan Magee Interviews - Modern Philosophy: Men of Ideas (1977-1978)

Number theory and algebra in Asia (b) | Math History | NJ Wildberger
After the later Alexandrian mathematicians Ptolemy and Diophantus, Greek mathematics went into decline and the focus shifted eastward. This lecture discusses some aspects of Chinese, Indian and Arab mathematics, in particular the interest in number theory (Pell's equation, the Chinese rema
From playlist MathHistory: A course in the History of Mathematics

Vidéo réalisée avec le soutien du projet AAMOT de l’ERC
From playlist Mathematics is a long conversation: a celebration of Barry Mazur

Lecture 18, Gregory of Nyssa, of PHL 354/CTI 335, History of Christian Philosophy, The University of Texas at Austin, Spring 2013
From playlist UT Austin: History of Christian Philosophy | CosmoLearning.org Philosophy

http://www.teachastronomy.com/ Pythagoras was one of the most influential thinkers in history. This Greek philosopher and mathematician came up with the idea that numbers were the basis of everything. There is no written record, and nothing about Pythagoras survives in writing. He essen
From playlist 02. Ancient Astronomy and Celestial Phenomena
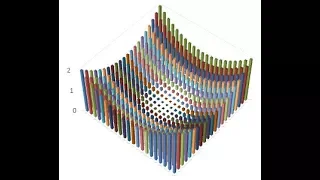
The Riemann integral for functions of two variables -- Calculus III
This lecture is on Calculus III. It follows Part III of the book Calculus Illustrated by Peter Saveliev. The text of the book can be found at http://calculus123.com.
From playlist Calculus III

http://www.teachastronomy.com/ Thales was a philosopher who lived in the 6th century B.C. in Miletus, in what is now Turkey. No written work by Thales survives, but we know that he kept accurate eclipse records and he speculated about astronomy. He decided that the source of all things w
From playlist 02. Ancient Astronomy and Celestial Phenomena

Greek Mathematics: Pythagoras and His Followers
Welcome to the History of Greek Mathematics mini-series! This series is a short introduction to Math History as a subject and the some of the important theorems created in ancient Greece. You are watching the second video in the series. If this series interested you check out our blog for
From playlist The History of Greek Mathematics: Math History

Jordan Peterson & The Meaning of Life | Philosophy Tube
Why this is Hell, nor are we out of it! Patreon: http://www.patreon.com/PhilosophyTube Subscribe! http://tinyurl.com/pr99a46 Paypal.me/PhilosophyTube Wanna get me a gift for the show? http://amzn.eu/5JAYdOd Check out my other videos on: Brexit: What is Democracy? https://www.youtube.co
From playlist The Main Show

Physical Science 1.1d - Copernicus Galileo Newton
A look at the ideas of Copernicus, Galileo, and Newton, and why they were revolutionary. These people put science on an experimental footing and ushered in the era of classical physics. From the Physical Science course by Derek Owens.
From playlist Physical Science Chapter 1 (Complete chapter)

Taylor Carman - “Narrative and Pictorial Truth”
Taylor Carman is Professor of Philosophy at Barnard College, Columbia University. He is the author of Heidegger’s Analytic: Interpretation, Discourse, and Authenticity in Being and Time and Merleau-Ponty and coeditor of The Cambridge Companion to Merleau-Ponty. He has written on topics in
From playlist Franke Lectures in the Humanities

Taming a Monster: The Master of Integration
Help me create more free content! =) https://www.patreon.com/mathable Merch :v - https://teespring.com/stores/papaflammy https://www.amazon.com/shop/flammablemaths https://shop.spreadshirt.de/papaflammy Become a Member of the Flammily! :0 https:
From playlist Integrals

Teach Astronomy - Early Greek Ideas
http://www.teachastronomy.com/ The early Greek philosophers had none of the tools of modern science. They did not have the machines with which to probe the atom. They did not have telescopes. They didn't have modern technology of any kind, and yet with logic and mathematics they were ab
From playlist 02. Ancient Astronomy and Celestial Phenomena

ICM 2006 Closing Round Table Are pure and applied mathematics drifting apart? Intervention by John Ball (Slides https://www.mathunion.org/fileadmin/IMU/Videos/ICM2006/tars/table2006_ball.pdf) Intervention by Lennart Carleson (Slides https://www.mathunion.org/fileadmin/IMU/Videos/ICM2006/
From playlist Number Theory