Euclidean plane geometry | Polygons
Polygon
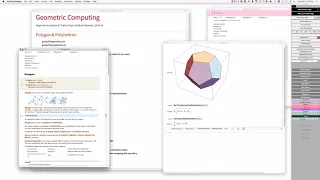
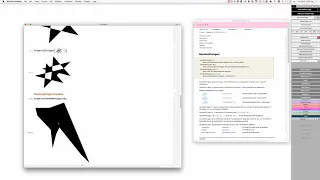
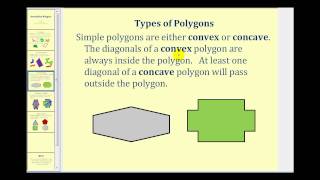
In geometry, a polygon (/ˈpɒlɪɡɒn/) is a plane figure that is described by a finite number of straight line segments connected to form a closed polygonal chain (or polygonal circuit). The bounded plane region, the bounding circuit, or the two together, may be called a polygon. The segments of a polygonal circuit are called its edges or sides. The points where two edges meet are the polygon's vertices (singular: vertex) or corners. The interior of a solid polygon is sometimes called its body. An n-gon is a polygon with n sides; for example, a triangle is a 3-gon. A simple polygon is one which does not intersect itself. Mathematicians are often concerned only with the bounding polygonal chains of simple polygons and they often define a polygon accordingly. A polygonal boundary may be allowed to cross over itself, creating star polygons and other self-intersecting polygons. A polygon is a 2-dimensional example of the more general polytope in any number of dimensions. There are many more defined for different purposes. (Wikipedia).