Affine geometry | Linear algebra
Affine space
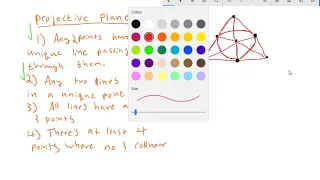
In mathematics, an affine space is a geometric structure that generalizes some of the properties of Euclidean spaces in such a way that these are independent of the concepts of distance and measure of angles, keeping only the properties related to parallelism and ratio of lengths for parallel line segments. In an affine space, there is no distinguished point that serves as an origin. Hence, no vector has a fixed origin and no vector can be uniquely associated to a point. In an affine space, there are instead displacement vectors, also called translation vectors or simply translations, between two points of the space. Thus it makes sense to subtract two points of the space, giving a translation vector, but it does not make sense to add two points of the space. Likewise, it makes sense to add a displacement vector to a point of an affine space, resulting in a new point translated from the starting point by that vector. Any vector space may be viewed as an affine space; this amounts to forgetting the special role played by the zero vector. In this case, elements of the vector space may be viewed either as points of the affine space or as displacement vectors or translations. When considered as a point, the zero vector is called the origin. Adding a fixed vector to the elements of a linear subspace (vector subspace) of a vector space produces an affine subspace. One commonly says that this affine subspace has been obtained by translating (away from the origin) the linear subspace by the translation vector (the vector added to all the elements of the linear space). In finite dimensions, such an affine subspace is the solution set of an inhomogeneous linear system. The displacement vectors for that affine space are the solutions of the corresponding homogeneous linear system, which is a linear subspace. Linear subspaces, in contrast, always contain the origin of the vector space. The dimension of an affine space is defined as the dimension of the vector space of its translations. An affine space of dimension one is an affine line. An affine space of dimension 2 is an affine plane. An affine subspace of dimension n – 1 in an affine space or a vector space of dimension n is an affine hyperplane. (Wikipedia).