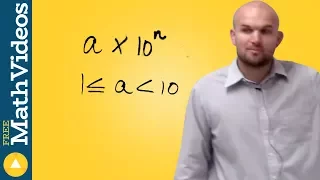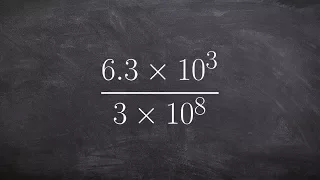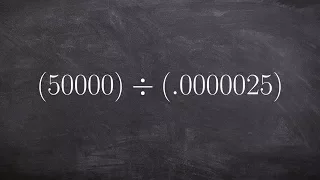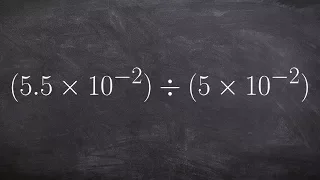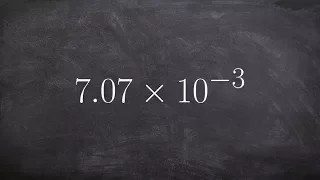Positional numeral systems | Articles containing proofs | Mathematical notation
Positional notation
Positional notation (or place-value notation, or positional numeral system) usually denotes the extension to any base of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system (or decimal system). More generally, a positional system is a numeral system in which the contribution of a digit to the value of a number is the value of the digit multiplied by a factor determined by the position of the digit. In early numeral systems, such as Roman numerals, a digit has only one value: I means one, X means ten and C a hundred (however, the value may be negated if placed before another digit). In modern positional systems, such as the decimal system, the position of the digit means that its value must be multiplied by some value: in 555, the three identical symbols represent five hundreds, five tens, and five units, respectively, due to their different positions in the digit string. The Babylonian numeral system, base 60, was the first positional system to be developed, and its influence is present today in the way time and angles are counted in tallies related to 60, such as 60 minutes in an hour and 360 degrees in a circle. Today, the Hindu–Arabic numeral system (base ten) is the most commonly used system globally. However, the binary numeral system (base two) is used in almost all computers and electronic devices because it is easier to implement efficiently in electronic circuits. Systems with negative base, complex base or negative digits have been described. Most of them do not require a minus sign for designating negative numbers. The use of a radix point (decimal point in base ten), extends to include fractions and allows representing any real number with arbitrary accuracy. With positional notation, arithmetical computations are much simpler than with any older numeral system; this led to the rapid spread of the notation when it was introduced in western Europe. (Wikipedia).