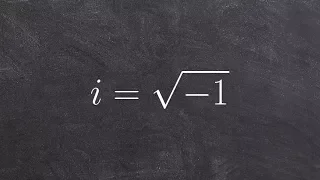Theory of computation | Computability theory
Computable number
In mathematics, computable numbers are the real numbers that can be computed to within any desired precision by a finite, terminating algorithm. They are also known as the recursive numbers, effective numbers or the computable reals or recursive reals. Equivalent definitions can be given using μ-recursive functions, Turing machines, or λ-calculus as the formal representation of algorithms. The computable numbers form a real closed field and can be used in the place of real numbers for many, but not all, mathematical purposes. (Wikipedia).