Elementary mathematics | Functions and mappings
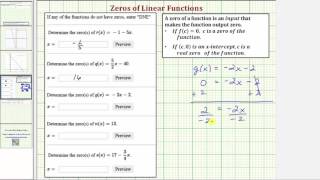
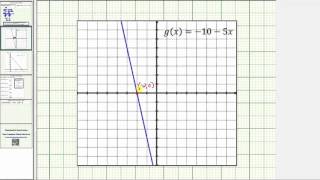
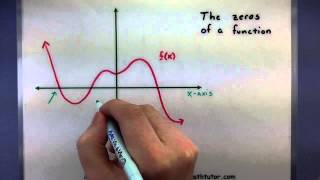
Zero of a function
In mathematics, a zero (also sometimes called a root) of a real-, complex-, or generally vector-valued function , is a member of the domain of such that vanishes at ; that is, the function attains the value of 0 at , or equivalently, is the solution to the equation . A "zero" of a function is thus an input value that produces an output of 0. A root of a polynomial is a zero of the corresponding polynomial function. The fundamental theorem of algebra shows that any non-zero polynomial has a number of roots at most equal to its degree, and that the number of roots and the degree are equal when one considers the complex roots (or more generally, the roots in an algebraically closed extension) counted with their multiplicities. For example, the polynomial of degree two, defined by has the two roots (or zeros) that are 2 and 3. If the function maps real numbers to real numbers, then its zeros are the -coordinates of the points where its graph meets the x-axis. An alternative name for such a point in this context is an -intercept. (Wikipedia).