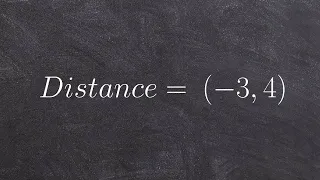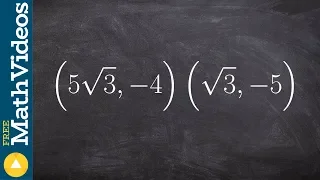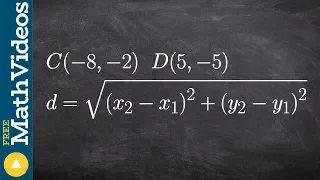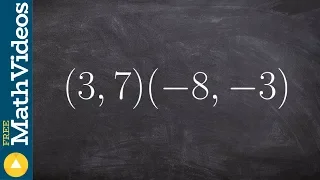Distance | Pythagorean theorem | Length | Metric geometry
Euclidean distance
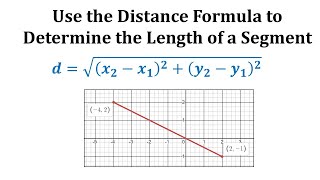
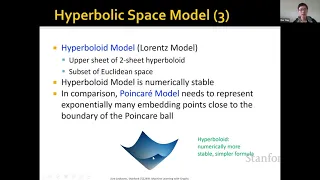
In mathematics, the Euclidean distance between two points in Euclidean space is the length of a line segment between the two points.It can be calculated from the Cartesian coordinates of the points using the Pythagorean theorem, therefore occasionally being called the Pythagorean distance. These names come from the ancient Greek mathematicians Euclid and Pythagoras, although Euclid did not represent distances as numbers, and the connection from the Pythagorean theorem to distance calculation was not made until the 18th century. The distance between two objects that are not points is usually defined to be the smallest distance among pairs of points from the two objects. Formulas are known for computing distances between different types of objects, such as the distance from a point to a line. In advanced mathematics, the concept of distance has been generalized to abstract metric spaces, and other distances than Euclidean have been studied. In some applications in statistics and optimization, the square of the Euclidean distance is used instead of the distance itself. (Wikipedia).