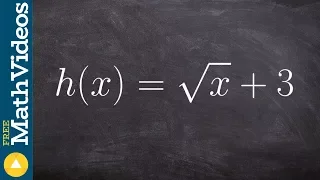Equation
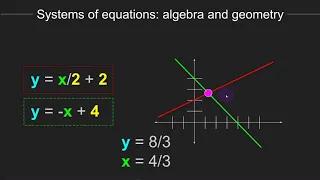
In mathematics, an equation is a formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign =. The word equation and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for example, in French an équation is defined as containing one or more variables, while in English, any well-formed formula consisting of two expressions related with an equals sign is an equation. Solving an equation containing variables consists of determining which values of the variables make the equality true. The variables for which the equation has to be solved are also called unknowns, and the values of the unknowns that satisfy the equality are called solutions of the equation. There are two kinds of equations: identities and conditional equations. An identity is true for all values of the variables. A conditional equation is only true for particular values of the variables. An equation is written as two expressions, connected by an equals sign ("="). The expressions on the two sides of the equals sign are called the "left-hand side" and "right-hand side" of the equation. Very often the right-hand side of an equation is assumed to be zero. Assuming this does not reduce the generality, as this can be realized by subtracting the right-hand side from both sides. The most common type of equation is a polynomial equation (commonly called also an algebraic equation) in which the two sides are polynomials.The sides of a polynomial equation contain one or more terms. For example, the equation has left-hand side , which has four terms, and right-hand side , consisting of just one term. The names of the variables suggest that x and y are unknowns, and that A, B, and C are parameters, but this is normally fixed by the context (in some contexts, y may be a parameter, or A, B, and C may be ordinary variables). An equation is analogous to a scale into which weights are placed. When equal weights of something (e.g., grain) are placed into the two pans, the two weights cause the scale to be in balance and are said to be equal. If a quantity of grain is removed from one pan of the balance, an equal amount of grain must be removed from the other pan to keep the scale in balance. More generally, an equation remains in balance if the same operation is performed on its both sides. In Cartesian geometry, equations are used to describe geometric figures. As the equations that are considered, such as implicit equations or parametric equations, have infinitely many solutions, the objective is now different: instead of giving the solutions explicitly or counting them, which is impossible, one uses equations for studying properties of figures. This is the starting idea of algebraic geometry, an important area of mathematics. Algebra studies two main families of equations: polynomial equations and, among them, the special case of linear equations. When there is only one variable, polynomial equations have the form P(x) = 0, where P is a polynomial, and linear equations have the form ax + b = 0, where a and b are parameters. To solve equations from either family, one uses algorithmic or geometric techniques that originate from linear algebra or mathematical analysis. Algebra also studies Diophantine equations where the coefficients and solutions are integers. The techniques used are different and come from number theory. These equations are difficult in general; one often searches just to find the existence or absence of a solution, and, if they exist, to count the number of solutions. Differential equations are equations that involve one or more functions and their derivatives. They are solved by finding an expression for the function that does not involve derivatives. Differential equations are used to model processes that involve the rates of change of the variable, and are used in areas such as physics, chemistry, biology, and economics. The "=" symbol, which appears in every equation, was invented in 1557 by Robert Recorde, who considered that nothing could be more equal than parallel straight lines with the same length. (Wikipedia).