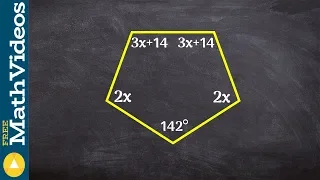
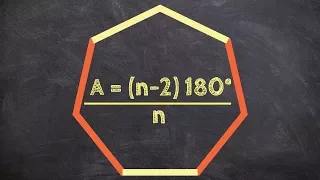
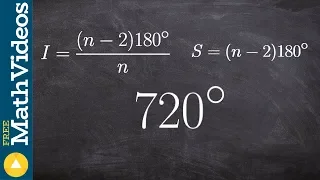Integral polytope
In geometry and polyhedral combinatorics, an integral polytope is a convex polytope whose vertices all have integer Cartesian coordinates. That is, it is a polytope that equals the convex hull of its integer points.Integral polytopes are also called lattice polytopes or Z-polytopes. The special cases of two- and three-dimensional integral polytopes may be called polygons or polyhedra instead of polytopes, respectively. (Wikipedia).