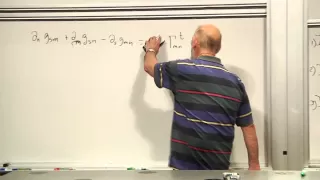Bernhard Riemann
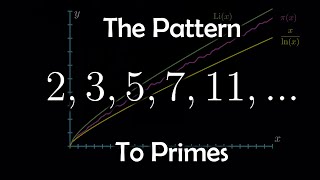
Georg Friedrich Bernhard Riemann (German: [ˈɡeːɔʁk ˈfʁiːdʁɪç ˈbɛʁnhaʁt ˈʁiːman]; 17 September 1826 – 20 July 1866) was a German mathematician who made contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry. In the field of real analysis, he is mostly known for the first rigorous formulation of the integral, the Riemann integral, and his work on Fourier series. His contributions to complex analysis include most notably the introduction of Riemann surfaces, breaking new ground in a natural, geometric treatment of complex analysis. His 1859 paper on the prime-counting function, containing the original statement of the Riemann hypothesis, is regarded as a foundational paper of analytic number theory. Through his pioneering contributions to differential geometry, Riemann laid the foundations of the mathematics of general relativity. He is considered by many to be one of the greatest mathematicians of all time. (Wikipedia).