Analytic geometry | Mathematical concepts | Elementary geometry
Line (geometry)
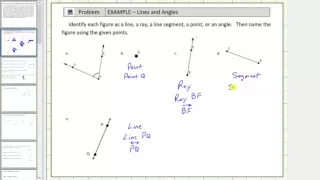
In geometry, a line is an infinitely long object with no width, depth, or curvature. Thus, lines are one-dimensional objects, though they may exist in two, three, or higher dimension spaces. The word line may also refer to a line segment in everyday life, which has two points to denote its ends. Lines can be referred by two points that lay on it (e.g., ) or by a single letter (e.g., ). Euclid described a line as "breadthless length" which "lies equally with respect to the points on itself"; he introduced several postulates as basic unprovable properties from which he constructed all of geometry, which is now called Euclidean geometry to avoid confusion with other geometries which have been introduced since the end of the 19th century (such as non-Euclidean, projective and affine geometry). In modern mathematics, given the multitude of geometries, the concept of a line is closely tied to the way the geometry is described. For instance, in analytic geometry, a line in the plane is often defined as the set of points whose coordinates satisfy a given linear equation, but in a more abstract setting, such as incidence geometry, a line may be an independent object, distinct from the set of points which lie on it. When a geometry is described by a set of axioms, the notion of a line is usually left undefined (a so-called primitive object). The properties of lines are then determined by the axioms which refer to them. One advantage to this approach is the flexibility it gives to users of the geometry. Thus in differential geometry, a line may be interpreted as a geodesic (shortest path between points), while in some projective geometries, a line is a 2-dimensional vector space (all linear combinations of two independent vectors). This flexibility also extends beyond mathematics and, for example, permits physicists to think of the path of a light ray as being a line. (Wikipedia).