Self-adjoint operators. All eigenvalues of a self-adjoint operator are real. On a complex vector space, if the inner product of Tv and v is real for every vector v, then T is self-adjoint.
From playlist Linear Algebra Done Right

Hermitian Operators (Self-Adjoint Operators) | Quantum Mechanics
In this video, we will talk about Hermitian operators in quantum mechanics. If an operator A is a Hermitian operator, then it is the same as its adjoint operator A-dagger, which is defined via this equation here. Usually, the terms "Hermitian" and "self adjoint" are used interchangeably, h
From playlist Quantum Mechanics, Quantum Field Theory

Normal operators. Characterization of normal operators by ||Tv|| = ||T*v|| for all v. Eigenvectors of a normal operator corresponding to distinct eigenvalues are orthogonal.
From playlist Linear Algebra Done Right

Adjoint / Daggered Operators in Quantum Mechanics
In this video, we will explain adjoint operators in quantum mechanics. First of all, for any operator A, we can define its adjoint, A-dagger, via this equation. The idea behind this is, that while operators in quantum mechanics usually act towards the right, adjoint operators act to the le
From playlist Quantum Mechanics, Quantum Field Theory
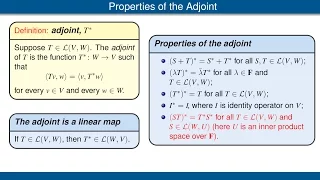
Algebraic properties of the adjoint. Null space and range of the adjoint. The matrix of T* is the conjugate transpose of the matrix of T.
From playlist Linear Algebra Done Right

이번 강의는 ' C언어 09강 연산자-II ' 편입니다. 바로가기: http://iotcenter.seoul.go.kr/648
From playlist c언어
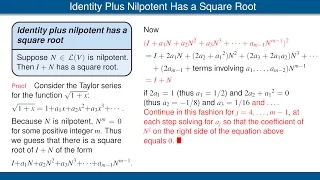
The identity operator plus a nilpotent operator has a square root. An invertible operator on a finite-dimensional complex vector space has a square root.
From playlist Linear Algebra Done Right

Lecture with Mads Jakobsen. Kapitler: 00:00 - Introduction; 00:30 - Homework; 04:30 - Normed Vector Spaces; 08:30 - The Adjoint Operator; 18:30 - Theorem 4.5.1; 19:30 - Proof; 24:00 - Lema 4.4.2; 32:30 - Example Week 2;
From playlist DTU: Mathematics 4 Real Analysis | CosmoLearning.org Math

Positive operators. Square roots of operators. Characterization of positive operators. Each positive operator has a unique positive square root.
From playlist Linear Algebra Done Right

Lara Ismert: "Heisenberg Pairs on Hilbert C*-modules"
Actions of Tensor Categories on C*-algebras 2021 "Heisenberg Pairs on Hilbert C*-modules" Lara Ismert - Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University, Mathematics Abstract: Roughly speaking, a Heisenberg pair on a Hilbert space is a pair of self-adjoint operators (A,B) which satisfy the Heisenber
From playlist Actions of Tensor Categories on C*-algebras 2021

Jens Kaad: Differentiable absorption of Hilbert C*-modules
The Kasparov absorption (or stabilization) theorem states that any countably generated Hilbert C^*-module is isomorphic to a direct summand in a standard module. In this talk, I will generalize this result by incorporating a densely defined derivation on the base C^*-algebra. The extra com
From playlist HIM Lectures: Trimester Program "Non-commutative Geometry and its Applications"
Kristin Courtney: C*-structure on images of completely positive order zero maps
Talk by Kristin Courtney in Global Noncommutative Geometry Seminar (Americas) http://www.math.wustl.edu/~xtang/NCG-Seminar.html on September 16, 2020.
From playlist Global Noncommutative Geometry Seminar (Americas)

Esteban Andruchow: Metric geometry in homogeneous spaces of the unitary group of a C∗-algebra. 1
Find this video and other talks given by worldwide mathematicians on CIRM's Audiovisual Mathematics Library: http://library.cirm-math.fr. And discover all its functionalities: - Chapter markers and keywords to watch the parts of your choice in the video - Videos enriched with abstracts, b
From playlist Analysis and its Applications

Lecture 22: The Spectral Theorem for a Compact Self-Adjoint Operator
MIT 18.102 Introduction to Functional Analysis, Spring 2021 Instructor: Dr. Casey Rodriguez View the complete course: https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/18-102-introduction-to-functional-analysis-spring-2021/ YouTube Playlist: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-sfaHVFWBU8&list=PLUl4u3cNGP63micsJp_
From playlist MIT 18.102 Introduction to Functional Analysis, Spring 2021

The analogy between the complex numbers and L(V). The Polar Decomposition: If T is an operator on a finite-dimensional inner product space V, then there exists an isometry on V such that T equals S times the square root of T*T.
From playlist Linear Algebra Done Right

Cristina Câmara: Truncated Toeplitz operators
Abstract: Toeplitz matrices and operators constitute one of the most important and widely studied classes of non-self-adjoint operators. In this talk we consider truncated Toeplitz operators, a natural generalisation of finite Toeplitz matrices. They appear in various contexts, such as the
From playlist Analysis and its Applications
Lazaro Recht: Metric geometry in homogeneous spaces of the unitary group of a C* -algebra. 2
Find this video and other talks given by worldwide mathematicians on CIRM's Audiovisual Mathematics Library: http://library.cirm-math.fr. And discover all its functionalities: - Chapter markers and keywords to watch the parts of your choice in the video - Videos enriched with abstracts, b
From playlist Algebraic and Complex Geometry