
The analogy between the complex numbers and L(V). The Polar Decomposition: If T is an operator on a finite-dimensional inner product space V, then there exists an isometry on V such that T equals S times the square root of T*T.
From playlist Linear Algebra Done Right

Seth Lloyd - Quantum polar decomposition - IPAM at UCLA
Recorded 25 January 2022. Seth Lloyd of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology presents "Quantum polar decomposition" at IPAM's Quantum Numerical Linear Algebra Workshop. Abstract: The polar decomposition decomposes a matrix into the product of a unitary and an Hermitian matrix. This ta
From playlist Quantum Numerical Linear Algebra - Jan. 24 - 27, 2022

Polar to rectangular equation conversion
Learn how to convert between rectangular and polar equations. A rectangular equation is an equation having the variables x and y which can be graphed in the rectangular cartesian plane. A polar equation is an equation defining an algebraic curve specified by r as a function of theta on the
From playlist Convert Between Polar/Rectangular (Equations) #Polar
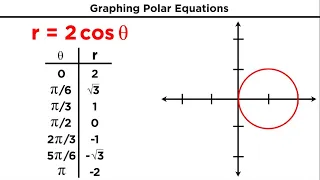
Polar Coordinates and Graphing Polar Equations
Everything we have done on the coordinate plane so far has been using rectangular coordinates. That's the x and y we are used to. But that's not the only coordinate system. We can also use polar coordinates, which graph points in terms of a radius, or distance from a pole, and theta, the a
From playlist Mathematics (All Of It)

Linear Algebra 23a: Polar Decomposition - A Product of an Orthogonal and Symmetric Matrices
https://bit.ly/PavelPatreon https://lem.ma/LA - Linear Algebra on Lemma http://bit.ly/ITCYTNew - Dr. Grinfeld's Tensor Calculus textbook https://lem.ma/prep - Complete SAT Math Prep
From playlist Part 3 Linear Algebra: Linear Transformations

Converting the Rectangular Equation x^2 + y^2 = 4 into Polar Form
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!! https://goo.gl/JQ8Nys Converting the Rectangular Equation x^2 + y^2 = 4 into Polar Form
From playlist Trigonometry
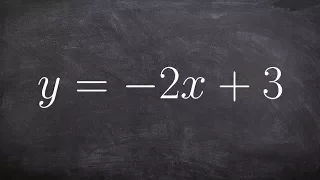
Converting a linear equation to polar form
Learn how to convert between rectangular and polar equations. A rectangular equation is an equation having the variables x and y which can be graphed in the rectangular cartesian plane. A polar equation is an equation defining an algebraic curve specified by r as a function of theta on the
From playlist Convert Between Polar/Rectangular (Equations) #Polar
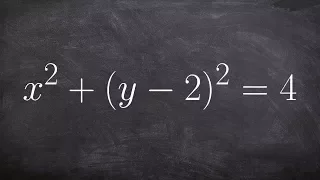
Rectangular to polar equation conversion
Learn how to convert between rectangular and polar equations. A rectangular equation is an equation having the variables x and y which can be graphed in the rectangular cartesian plane. A polar equation is an equation defining an algebraic curve specified by r as a function of theta on the
From playlist Convert Between Polar/Rectangular (Equations) #Polar
Mumford-Tate Groups and Domains - Phillip Griffiths
Phillip Griffiths Professor Emeritus, School of Mathematics March 28, 2011 For more videos, visit http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

Inaugural Imaging & Inverse Problems (IMAGINE) OneWorld SIAM-IS Virtual Seminar Series Talk
Date: Wednesday, October 14, 10:00am EDT Speaker: Michael Friedlander, University of British Columbia Title: Polar deconvolution of mixed signals Abstract: The signal demixing problem seeks to separate the superposition of multiple signals into its constituent components. We model the s
From playlist Imaging & Inverse Problems (IMAGINE) OneWorld SIAM-IS Virtual Seminar Series
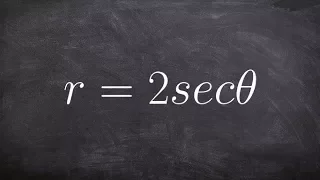
Write a rectangular equation in polar form
Learn how to convert between rectangular and polar equations. A rectangular equation is an equation having the variables x and y which can be graphed in the rectangular cartesian plane. A polar equation is an equation defining an algebraic curve specified by r as a function of theta on the
From playlist Convert Between Polar/Rectangular (Equations) #Polar

https://www.math.ias.edu/files/media/agenda.pdf More videos on http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

Determinantal varieties and asymptotic expansion of Bergman kernels by Harald Upmeier
DISCUSSION MEETING ANALYTIC AND ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY DATE:19 March 2018 to 24 March 2018 VENUE:Madhava Lecture Hall, ICTS, Bangalore. Complex analytic geometry is a very broad area of mathematics straddling differential geometry, algebraic geometry and analysis. Much of the interactions be
From playlist Analytic and Algebraic Geometry-2018

Relativistic Spin Hydrodynamics by Amaresh Jaiswal
DISCUSSION MEETING EXTREME NONEQUILIBRIUM QCD (ONLINE) ORGANIZERS: Ayan Mukhopadhyay (IIT Madras) and Sayantan Sharma (IMSc Chennai) DATE & TIME: 05 October 2020 to 09 October 2020 VENUE: Online Understanding quantum gauge theories is one of the remarkable challenges of the millennium
From playlist Extreme Nonequilibrium QCD (Online)

Matrix with complex eigenvalues and diagonalization. Featuring polar decomposition, which is like polar coordinates, but for matrices. Check out my Eigenvalues playlist: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H-NxPABQlxI&list=PLJb1qAQIrmmC72x-amTHgG-H_5S19jOSf Subscribe to my channel: https://w
From playlist Eigenvalues
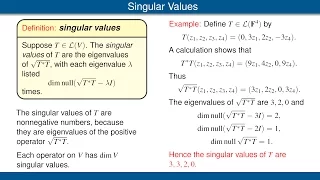
Singular values. The Singular Value Decomposition.
From playlist Linear Algebra Done Right

Solve a System of Linear Equations Using LU Decomposition
This video explains how to use LU Decomposition to solve a system of linear equations. Site: http://mathispower4u.com Blog: http://mathispower4u.wordpress.com
From playlist Matrix Equations
