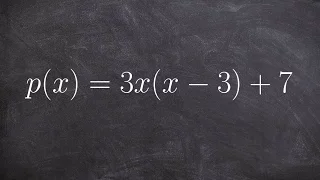
Multiplying polynomials to write in standard form and label the degree and LC
👉 Learn how to find the degree and the leading coefficient of a polynomial expression. The degree of a polynomial expression is the the highest power (exponent) of the individual terms that make up the polynomial. For terms with more that one variable, the power (exponent) of the term is t
From playlist Find the leading coefficient and degree of a polynomial | simplify first
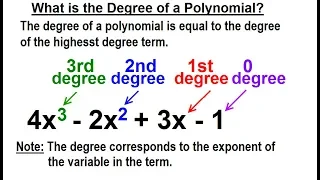
Algebra - Ch. 5: Polynomials (2 of 32) What is the Degree of a Polynomial?
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will explain what are 0, 1st, 2nd, and 3rd degree polynomials. Note: the degree corresponds to the exponent of the variable in the term. To donate: http://www.ilectureonline.com/donate https://www.patreon
From playlist ALGEBRA CH 5 POLYNOMIALS
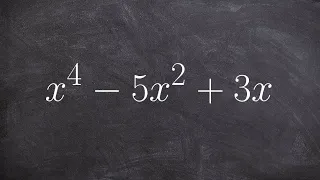
How do you find the degree of a polynomial
👉 Learn how to find the degree and the leading coefficient of a polynomial expression. The degree of a polynomial expression is the highest power (exponent) of the individual terms that make up the polynomial. For terms with more that one variable, the power (exponent) of the term is the s
From playlist Find the leading coefficient and degree of a polynomial | expression
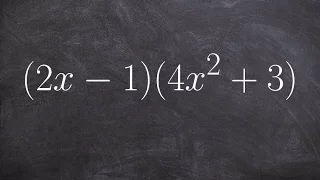
Determine LC and degree by multiplying binomials
👉 Learn how to find the degree and the leading coefficient of a polynomial expression. The degree of a polynomial expression is the the highest power (exponent) of the individual terms that make up the polynomial. For terms with more that one variable, the power (exponent) of the term is t
From playlist Find the leading coefficient and degree of a polynomial | simplify first

Solving Polynomial Equations Graphically
http://mathispower4u.wordpress.com/
From playlist Solving Polynomial Equations / Increasing and Decreasing Polynomials
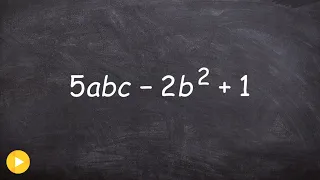
How to find the degree and leading coefficient of a polynomial (mistake)
👉 Learn how to find the degree and the leading coefficient of a polynomial expression. The degree of a polynomial expression is the highest power (exponent) of the individual terms that make up the polynomial. For terms with more that one variable, the power (exponent) of the term is the s
From playlist Find the leading coefficient and degree of a polynomial | expression

Apply operations and then write the polynomial in standard form and find degree and LC
👉 Learn how to find the degree and the leading coefficient of a polynomial expression. The degree of a polynomial expression is the the highest power (exponent) of the individual terms that make up the polynomial. For terms with more that one variable, the power (exponent) of the term is t
From playlist Find the leading coefficient and degree of a polynomial | simplify first
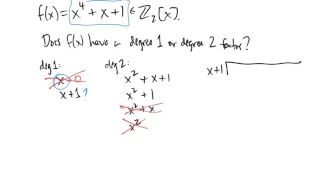
In this video I discuss irreducible polynomials and tests for irreducibility. Note that this video is intended for students in abstract algebra and is not appropriate for high-school or early college level algebra courses.
From playlist Abstract Algebra

Write the polynomial in standard form and determine the degree and LC
👉 Learn how to find the degree and the leading coefficient of a polynomial expression. The degree of a polynomial expression is the the highest power (exponent) of the individual terms that make up the polynomial. For terms with more that one variable, the power (exponent) of the term is t
From playlist Find the leading coefficient and degree of a polynomial | equation

Introduction to Polynomials (TTP Video 64)
https://www.patreon.com/ProfessorLeonard An explanation of the creation of polynomials and some of there properties.
From playlist To The Point Math (TTP Videos)

Marina Iliopoulou: Three polynomial methods for point counting, Lecture II
During these lectures, we will describe (a) the polynomial method that Dvir developed to solve the Kakeya problem in finite fields, (b) polynomial partitioning, developed by Guth and Katz to solve the Erdös distinct distances problem in the plane, and (c) the slice rank method, developed b
From playlist Harmonic Analysis and Analytic Number Theory

A nearly optimal lower bound on the approximate degree of AC00- Mark Bun
Computer Science/Discrete Mathematics Seminar I Topic: A nearly optimal lower bound on the approximate degree of AC00 Speaker: A nearly optimal lower bound on the approximate degree of AC00 Speaker: Mark Bun Affiliation: Princeton University Date: October 23, 2017 For more videos, pleas
From playlist Mathematics

Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.3: Polynomials and irreducibility
Visual Group Theory, Lecture 6.3: Polynomials and irreducibility A complex number is algebraic over Q (the rationals) if it is the root of a polynomial with rational coefficients. It is clear that every number that can be written with arithmetic and radicals is rational. Galois' big achie
From playlist Visual Group Theory

Write a polynomial in descending power order then label the degree and LC
👉 Learn how to find the degree and the leading coefficient of a polynomial expression. The degree of a polynomial expression is the highest power (exponent) of the individual terms that make up the polynomial. For terms with more that one variable, the power (exponent) of the term is the s
From playlist Find the leading coefficient and degree of a polynomial | expression
CSDM - Rafael Oliveira - October 12, 2015
http://www.math.ias.edu/calendar/event/83504/1444662900/1444666500
From playlist Computer Science/Discrete Mathematics

Some closure results for polynomial factorization - Mrinal Kumar
Computer Science/Discrete Mathematics Seminar II Topic: Some closure results for polynomial factorization Speaker: Mrinal Kumar Affiliation: Harvard University Date: Febuary 20, 2018 For more videos, please visit http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

Irreducibility (Eisenstein's Irreducibility Criterion)
Given a polynomial with integer coefficients, we can determine whether it's irreducible over the rationals using Eisenstein's Irreducibility Criterion. Unlike some our other technique, this works for polynomials of high degree! The tradeoff is that it works over the rationals, but need not
From playlist Modern Algebra - Chapter 11

Marina Iliopoulou: Three polynomial methods for point counting, Lecture I
During these lectures, we will describe (a) the polynomial method that Dvir developed to solve the Kakeya problem in finite fields, (b) polynomial partitioning, developed by Guth and Katz to solve the Erdös distinct distances problem in the plane, and (c) the slice rank method, developed b
From playlist Harmonic Analysis and Analytic Number Theory

Polynomials intro | Mathematics II | High School Math | Khan Academy
Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/algebra/x2f8bb11595b61c86:quadratics-multiplying-factoring/x2f8bb11595b61c86:multiply-monomial-polynomial/v/polynomials-intro Polynomials are sums of terms of the
From playlist Mathematics II | High School Math | Khan Academy

Ex: Find Key Information about a Given Polynomial Function
This video explains how to write a polynomial function in descending order, find the leading coefficient, give the degree, find the maximum number of x-intercepts, and the maximum number of turns. Site: http://mathispower4u.com Blog: http://mathispower4u.wordpress.com
From playlist Determining the Characteristics of Polynomial Functions