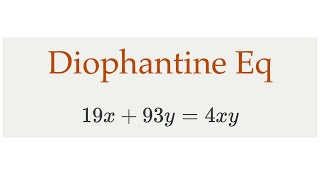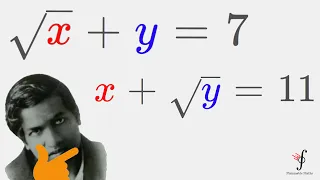Diophantine equation
In mathematics, a Diophantine equation is an equation, typically a polynomial equation in two or more unknowns with integer coefficients, such that the only solutions of interest are the integer ones. A linear Diophantine equation equates to a constant the sum of two or more monomials, each of degree one. An exponential Diophantine equation is one in which unknowns can appear in exponents. Diophantine problems have fewer equations than unknowns and involve finding integers that solve simultaneously all equations. As such systems of equations define algebraic curves, algebraic surfaces, or, more generally, algebraic sets, their study is a part of algebraic geometry that is called Diophantine geometry. The word Diophantine refers to the Hellenistic mathematician of the 3rd century, Diophantus of Alexandria, who made a study of such equations and was one of the first mathematicians to introduce symbolism into algebra. The mathematical study of Diophantine problems that Diophantus initiated is now called Diophantine analysis. While individual equations present a kind of puzzle and have been considered throughout history, the formulation of general theories of Diophantine equations (beyond the case of linear and quadratic equations) was an achievement of the twentieth century. (Wikipedia).