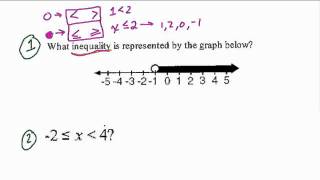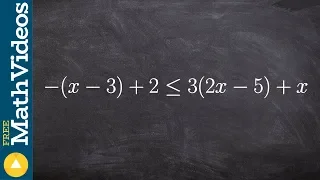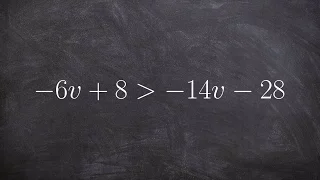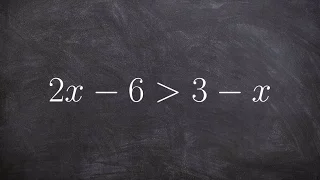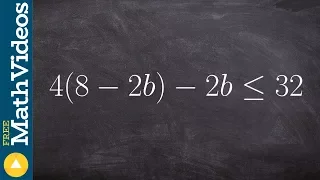Inequalities | Elementary algebra | Mathematical terminology
Inequality (mathematics)
In mathematics, an inequality is a relation which makes a non-equal comparison between two numbers or other mathematical expressions. It is used most often to compare two numbers on the number line by their size. There are several different notations used to represent different kinds of inequalities: * The notation a < b means that a is less than b. * The notation a > b means that a is greater than b. In either case, a is not equal to b. These relations are known as strict inequalities, meaning that a is strictly less than or strictly greater than b. Equivalence is excluded. In contrast to strict inequalities, there are two types of inequality relations that are not strict: * The notation a ≤ b or a ⩽ b means that a is less than or equal to b (or, equivalently, at most b, or not greater than b). * The notation a ≥ b or a ⩾ b means that a is greater than or equal to b (or, equivalently, at least b, or not less than b). The relation not greater than can also be represented by a ≯ b, the symbol for "greater than" bisected by a slash, "not". The same is true for not less than and a ≮ b. The notation a ≠ b means that a is not equal to b; this inequation sometimes is considered a form of strict inequality. It does not say that one is greater than the other; it does not even require a and b to be member of an ordered set. In engineering sciences, less formal use of the notation is to state that one quantity is "much greater" than another, normally by several orders of magnitude. * The notation a ≪ b means that a is much less than b. * The notation a ≫ b means that a is much greater than b. This implies that the lesser value can be neglected with little effect on the accuracy of an approximation (such as the case of ultrarelativistic limit in physics). In all of the cases above, any two symbols mirroring each other are symmetrical; a < b and b > a are equivalent, etc. (Wikipedia).