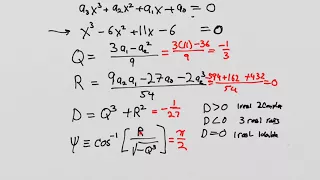Polynomials | Elementary algebra
Cubic equation
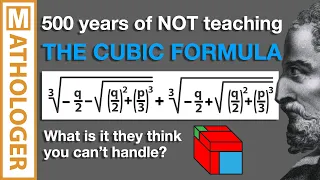
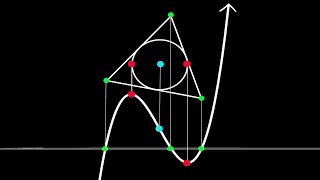
In algebra, a cubic equation in one variable is an equation of the form in which a is nonzero. The solutions of this equation are called roots of the cubic function defined by the left-hand side of the equation. If all of the coefficients a, b, c, and d of the cubic equation are real numbers, then it has at least one real root (this is true for all odd-degree polynomial functions). All of the roots of the cubic equation can be found by the following means: * algebraically, that is, they can be expressed by a cubic formula involving the four coefficients, the four basic arithmetic operations and nth roots (radicals). (This is also true of quadratic (second-degree) and quartic (fourth-degree) equations, but not of higher-degree equations, by the Abel–Ruffini theorem.) * trigonometrically * numerical approximations of the roots can be found using root-finding algorithms such as Newton's method. The coefficients do not need to be real numbers. Much of what is covered below is valid for coefficients in any field with characteristic other than 2 and 3. The solutions of the cubic equation do not necessarily belong to the same field as the coefficients. For example, some cubic equations with rational coefficients have roots that are irrational (and even non-real) complex numbers. (Wikipedia).