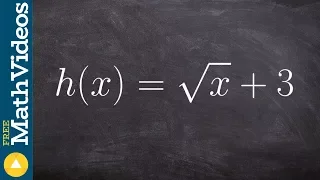Linear equation
In mathematics, a linear equation is an equation that may be put in the form where are the variables (or unknowns), and are the coefficients, which are often real numbers. The coefficients may be considered as parameters of the equation, and may be arbitrary expressions, provided they do not contain any of the variables. To yield a meaningful equation, the coefficients are required to not all be zero. Alternatively, a linear equation can be obtained by equating to zero a linear polynomial over some field, from which the coefficients are taken. The solutions of such an equation are the values that, when substituted for the unknowns, make the equality true. In the case of just one variable, there is exactly one solution (provided that ). Often, the term linear equation refers implicitly to this particular case, in which the variable is sensibly called the unknown. In the case of two variables, each solution may be interpreted as the Cartesian coordinates of a point of the Euclidean plane. The solutions of a linear equation form a line in the Euclidean plane, and, conversely, every line can be viewed as the set of all solutions of a linear equation in two variables. This is the origin of the term linear for describing this type of equations. More generally, the solutions of a linear equation in n variables form a hyperplane (a subspace of dimension n − 1) in the Euclidean space of dimension n. Linear equations occur frequently in all mathematics and their applications in physics and engineering, partly because non-linear systems are often well approximated by linear equations. This article considers the case of a single equation with coefficients from the field of real numbers, for which one studies the real solutions. All of its content applies to complex solutions and, more generally, for linear equations with coefficients and solutions in any field. For the case of several simultaneous linear equations, see system of linear equations. (Wikipedia).