Vector calculus | Orthogonality | Surfaces
Normal (geometry)
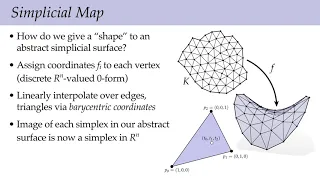
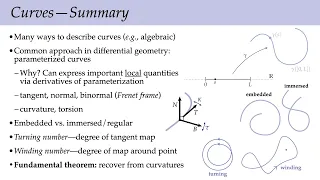
In geometry, a normal is an object such as a line, ray, or vector that is perpendicular to a given object. For example, the normal line to a plane curve at a given point is the (infinite) line perpendicular to the tangent line to the curve at the point.A normal vector may have length one (a unit vector) or its length may represent the curvature of the object (a curvature vector); its algebraic sign may indicate sides (interior or exterior). In three dimensions, a surface normal, or simply normal, to a surface at point is a vector perpendicular to the tangent plane of the surface at P. The word "normal" is also used as an adjective: a line normal to a plane, the normal component of a force, the normal vector, etc. The concept of normality generalizes to orthogonality (right angles). The concept has been generalized to differentiable manifolds of arbitrary dimension embedded in a Euclidean space. The normal vector space or normal space of a manifold at point is the set of vectors which are orthogonal to the tangent space at Normal vectors are of special interest in the case of smooth curves and smooth surfaces. The normal is often used in 3D computer graphics (notice the singular, as only one normal will be defined) to determine a surface's orientation toward a light source for flat shading, or the orientation of each of the surface's corners (vertices) to mimic a curved surface with Phong shading. The foot of a normal at a point of interest Q (analogous to the foot of a perpendicular) can be defined at the point P on the surface where the normal vector contains Q.The normal distance of a point Q to a curve or to a surface is the Euclidean distance between Q and its foot P. (Wikipedia).