
Math 060 Fall 2017 111317C Orthonormal Bases
Motivation: how to obtain the coordinate vector with respect to a given basis? Definition: orthogonal set. Example. Orthogonal implies linearly independent. Orthonormal sets. Example of an orthonormal set. Definition: orthonormal basis. Properties of orthonormal bases. Example: Fou
From playlist Course 4: Linear Algebra (Fall 2017)

Linear Algebra: Orthonormal Basis
Learn the basics of Linear Algebra with this series from the Worldwide Center of Mathematics. Find more math tutoring and lecture videos on our channel or at http://centerofmath.org/ More on unit vectors: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C6EYJVBYXIo
From playlist Basics: Linear Algebra

Orthonormal bases. The Gram-Schmidt Procedure. Schuur's Theorem on upper-triangular matrix with respect to an orthonormal basis. The Riesz Representation Theorem.
From playlist Linear Algebra Done Right

Linear Algebra 10: Construction of a Orthonormal Basis (Ch4 Pr3)
How to use the Gram-Schmidt orthogonalisation process to find a orthonormal basis on the space of degree two polynomials. Presented by Peter Brown from the UNSW School of Mathematics and Statistics.
From playlist MATH2501 - Linear Algebra

Orthogonal and Orthonormal Sets of Vectors
This video defines orthogonal and orthonormal sets of vectors.
From playlist Orthogonal and Orthonormal Sets of Vectors

Orthogonality and Orthonormality
We know that the word orthogonal is kind of like the word perpendicular. It implies that two vectors have an angle of ninety degrees or half pi radians between them. But this term means much more than this, as we can have orthogonal matrices, or entire subspaces that are orthogonal to one
From playlist Mathematics (All Of It)
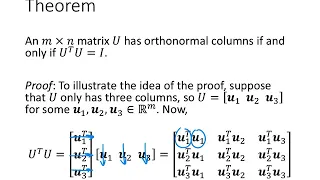
Linear Algebra - Lecture 39 - Orthonormal Sets
In this lecture, we discuss orthonormal sets of vectors. We investigate matrices with orthonormal columns. We also define an orthogonal matrix.
From playlist Linear Algebra Lectures

Linear Algebra: Given an orthonormal basis of R^n, we present a quick method for finding coefficients of linear combination in terms of the basis. We also give an analogue of Parseval's Identity, which relates these coefficients to the squared length of the vector.
From playlist MathDoctorBob: Linear Algebra I: From Linear Equations to Eigenspaces | CosmoLearning.org Mathematics

Math 060 Fall 2017 111517C Orthonormal Bases, Orthogonal Matrices, and Method of Least Squares
Definition of orthogonal matrices. Example: rotation matrix. Properties: Q orthogonal if and only if its transpose is its inverse. Q orthogonal implies it is an isometry; that it is isogonal (preserves angles). Theorem: How to find, given a vector in an inner product space, the closest
From playlist Course 4: Linear Algebra (Fall 2017)
Algebra 1M - international Course no. 104016 Dr. Aviv Censor Technion - International school of engineering
From playlist Algebra 1M

Lecture 15: Orthonormal Bases and Fourier Series
MIT 18.102 Introduction to Functional Analysis, Spring 2021 Instructor: Dr. Casey Rodriguez View the complete course: https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/18-102-introduction-to-functional-analysis-spring-2021/ YouTube Playlist: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yb69dAq4uh8&list=PLUl4u3cNGP63micsJp_
From playlist MIT 18.102 Introduction to Functional Analysis, Spring 2021

Linear Algebra 6.3 Gram-Schmidt Process; QR-Decomposition
My notes are available at http://asherbroberts.com/ (so you can write along with me). Elementary Linear Algebra: Applications Version 12th Edition by Howard Anton, Chris Rorres, and Anton Kaul A. Roberts is supported in part by the grants NSF CAREER 1653602 and NSF DMS 2153803.
From playlist Linear Algebra
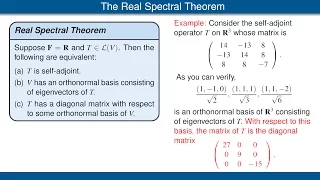
The Complex Spectral Theorem and the Real Spectral Theorem, with examples.
From playlist Linear Algebra Done Right

Coordinates with respect to orthonormal bases | Linear Algebra | Khan Academy
Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/linear-algebra/alternate-bases/orthonormal-basis/v/linear-algebra-coordinates-with-respect-to-orthonormal-bases Seeing that orthonormal bases make for good coordin
From playlist Alternate coordinate systems (bases) | Linear Algebra | Khan Academy

17. Orthogonal Matrices and Gram-Schmidt
MIT 18.06 Linear Algebra, Spring 2005 Instructor: Gilbert Strang View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/18-06S05 YouTube Playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLE7DDD91010BC51F8 17. Orthogonal Matrices and Gram-Schmidt License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information a
From playlist MIT 18.06 Linear Algebra, Spring 2005

Lecture 19: Compact Subsets of a Hilbert Space and Finite-Rank Operators
MIT 18.102 Introduction to Functional Analysis, Spring 2021 Instructor: Dr. Casey Rodriguez View the complete course: https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/18-102-introduction-to-functional-analysis-spring-2021/ YouTube Playlist: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PBMyBVPRtKA&list=PLUl4u3cNGP63micsJp_
From playlist MIT 18.102 Introduction to Functional Analysis, Spring 2021

The Gram-Schmidt process | Alternate coordinate systems (bases) | Linear Algebra | Khan Academy
Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/linear-algebra/alternate-bases/orthonormal-basis/v/linear-algebra-the-gram-schmidt-process Finding an orthonormal basis for a subspace using the Gram-Schmidt Proce
From playlist Alternate coordinate systems (bases) | Linear Algebra | Khan Academy
Math 139 Fourier Analysis Lecture 31: Fourier Analysis on Finite Abelian Groups
Finite abelian groups; characters; dual group. Characters form an orthonormal family: cancellation property (moment condition) of characters; proof of orthonormality; the dual group is an orthonormal basis for the space of functions on the group. Linear algebra: spectral theorem (given a
From playlist Course 8: Fourier Analysis

RT8.2. Finite Groups: Classification of Irreducibles
Representation Theory: Using the Schur orthogonality relations, we obtain an orthonormal basis of L^2(G) using matrix coefficients of irreducible representations. This shows the sum of squares of dimensions of irreducibles equals |G|. We also obtain an orthonormal basis of Class(G) usin
From playlist Representation Theory