Group actions (mathematics) | Dynamical systems
Orbit (dynamics)
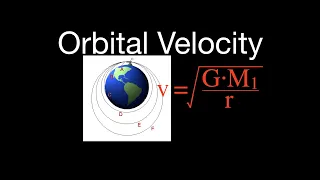
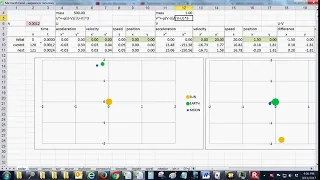
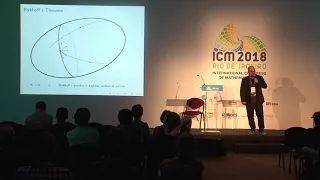
In mathematics, specifically in the study of dynamical systems, an orbit is a collection of points related by the evolution function of the dynamical system. It can be understood as the subset of phase space covered by the trajectory of the dynamical system under a particular set of initial conditions, as the system evolves. As phase space trajectory is uniquely determined for any given set of phase space coordinates, it is not possible for different orbits to intersect in phase space, therefore the set of all orbits of a dynamical system is a partition of the phase space. Understanding the properties of orbits by using topological methods is one of the objectives of the modern theory of dynamical systems. For discrete-time dynamical systems, the orbits are sequences; for real dynamical systems, the orbits are curves; and for holomorphic dynamical systems, the orbits are Riemann surfaces. (Wikipedia).