Logic: The Structure of Reason
As a tool for characterizing rational thought, logic cuts across many philosophical disciplines and lies at the core of mathematics and computer science. Drawing on Aristotle’s Organon, Russell’s Principia Mathematica, and other central works, this program tracks the evolution of logic, be
From playlist Logic & Philosophy of Mathematics

An introduction to the general types of logic statements
From playlist Geometry

Simplify the Negation of Statements with Quantifiers and Predicates
This video provides two examples of how to determine simplified logically equivalent statements containing quantifiers and predicates. mathispower4u.com
From playlist Symbolic Logic and Proofs (Discrete Math)

Maths for Programmers: Logic (What Is Logic?)
We're busy people who learn to code, then practice by building projects for nonprofits. Learn Full-stack JavaScript, build a portfolio, and get great references with our open source community. Join our community at https://freecodecamp.com Follow us on twitter: https://twitter.com/freecod
From playlist Maths for Programmers

Definition of Continuity in Calculus Explanation and Examples
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!! https://goo.gl/JQ8Nys Definition of Continuity in Calculus Explanation and Examples. - Definition of continuity at a point. - Explanation of the definition. - Examples of functions where the definition fails.
From playlist Calculus 1 Exam 1 Playlist

Introduction to Predicate Logic
This video introduces predicate logic. mathispower4u.com
From playlist Symbolic Logic and Proofs (Discrete Math)

Mathematical Statements and Logic Connectives
This video defines mathematical statements and logic connectives.
From playlist Mathematical Statements (Discrete Math)

Logic for Programmers: Propositional Logic
Logic is the foundation of all computer programming. In this video you will learn about propositional logic. 🔗Homework: http://www.codingcommanders.com/logic.php 🎥Logic for Programmers Playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLWKjhJtqVAbmqk3-E3MPFVoWMufdbR4qW 🔗Check out the Cod
From playlist Logic for Programmers

Recursively Defined Sets - An Intro
Recursively defined sets are an important concept in mathematics, computer science, and other fields because they provide a framework for defining complex objects or structures in a simple, iterative way. By starting with a few basic objects and applying a set of rules repeatedly, we can g
From playlist All Things Recursive - with Math and CS Perspective

Find this video and other talks given by worldwide mathematicians on CIRM's Audiovisual Mathematics Library: http://library.cirm-math.fr. And discover all its functionalities: - Chapter markers and keywords to watch the parts of your choice in the video - Videos enriched with abstracts, b
From playlist Mathematical Aspects of Computer Science

Nicole Schweikardt: Databases and descriptive complexity – lecture 1
Recording during the meeting "Spring school on Theoretical Computer Science (EPIT) - Databases, Logic and Automata " the April 11, 2019 at the Centre International de Rencontres Mathématiques (Marseille, France) Filmmaker: Guillaume Hennenfent Find this video and other talks given by wor
From playlist Numerical Analysis and Scientific Computing

Thomas Colcombet : Algebra vs Logic over (generalised) words
CONFERENCE Recording during the thematic meeting : « Discrete mathematics and logic: between mathematics and the computer science » the January 17, 2023 at the Centre International de Rencontres Mathématiques (Marseille, France) Filmmaker: Jean Petit Find this video and other talks give
From playlist Logic and Foundations

George F. R. Ellis - What Is Strong Emergence?
The world works at different levels — fundamental physics, physics, chemistry, biology, psychology, sociology — with each level having its own rules and regularities. Here’s the deep question: Ultimately, can what happens at a higher level be explained entirely in terms of what happens at
From playlist Closer To Truth - George F. R. Ellis Interviews
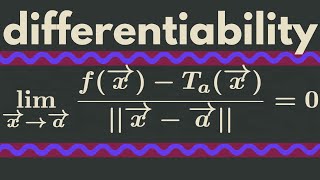
Multivariable Calculus | Differentiability
We give the definition of differentiability for a multivariable function and provide a few examples. http://www.michael-penn.net https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Michael_Penn5 http://www.randolphcollege.edu/mathematics/
From playlist Multivariable Calculus

Damiano Mazza: Heterodox exponential modalities in linear logic
HYBRID EVENT Recorded during the meeting Linear Logic Winter School" the January 28, 2022 by the Centre International de Rencontres Mathématiques (Marseille, France) Filmmaker: Guillaume Hennenfent Find this video and other talks given by worldwide mathematicians on CIRM's Audiovisual
From playlist Logic and Foundations