
Multiplying and Dividing Negative Numbers
"Multiply or divide a mixture of positive and negative numbers."
From playlist Number: Negative Numbers
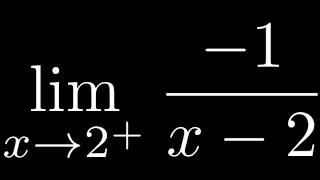
How to Compute a One Sided limit as x approaches from the right
In this video I will show you How to Compute a One Sided limit as x approaches from the right.
From playlist One-sided Limits

Ex: Linear Equation Application with One Variable - Number Problem
This video provides and example of how to solve a number problem using a linear equation with one variable. One number is a multiple of the other. The difference is a constant. Find the two numbers. Library: http://mathispower4u.com Search: http://mathispower4u.wordpress.com
From playlist Whole Number Applications

This video explains how to divide whole numbers and decimals by powers of ten. Search Video Library at http://www.mathispower4u.wordpress.com
From playlist Number Sense - Decimals, Percents, and Ratios

Zero Factorial: Why is 0! = 1?
This video provides justification as to why 0!=1 using patterns and the meaning of a permutation. http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Using the Binomial Theorem / Combinations
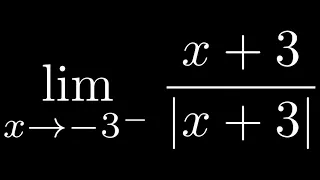
Computing a One Sided Limit with an Absolute Value Function
In this video I do an example of Computing a One Sided Limit with an Absolute Value Function.
From playlist One-sided Limits

This video explains how to multiply using whole numbers. http://mathispower4u.yolasite.com/
From playlist Multiplying and Dividing Whole Numbers

Thanks to all of you who support me on Patreon. You da real mvps! $1 per month helps!! :) https://www.patreon.com/patrickjmt !! Limits Involving Fractions. Here we have a 0/0 type of limit which we can evaluate by simplifying the fraction.
From playlist All Videos - Part 3

From playlist Mathematics of Sharing

26. Chemical and biological oxidation/reduction reactions
MIT 5.111 Principles of Chemical Science, Fall 2008 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/5-111F08 Instructor: Catherine Drennan, Elizabeth Vogel Taylor License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT 5.111 Principles of Chemical Science, Fall 2008

On some fine-grained questions in algorithms and complexity – V. Vassilevska Williams – ICM2018
Mathematical Aspects of Computer Science Invited Lecture 14.8 On some fine-grained questions in algorithms and complexity Virginia Vassilevska Williams Abstract: In recent years, a new “fine-grained” theory of computational hardness has been developed, based on “fine-grained reductions”
From playlist Mathematical Aspects of Computer Science

Bala Krishnamoorthy (10/20/20): Dimension reduction: An overview
Bala Krishnamoorthy (10/20/20): Dimension reduction: An overview Title: Dimension reduction: An overview Abstract: We present a broad overview of various dimension reduction techniques. Referred to also as manifold learning, we review linear dimension reduction techniques, e.g., principa
From playlist Tutorials

NP Completeness III - More Reductions - Lecutre 17
All rights reserved for http://www.aduni.org/ Published under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike license http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/ Tutorials by Instructor: Shai Simonson. http://www.stonehill.edu/compsci/shai.htm Visit the forum at: http://www.coderisland.c
From playlist ArsDigita Algorithms by Shai Simonson

Lec 25 | MIT 5.111 Principles of Chemical Science, Fall 2005
Oxidation/Reduction (Prof. Catherine Drennan) View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/5-111F05 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT 5.111 Principles of Chemical Science, Fall 2005

General Chemistry 1C. Lecture 16. Electrochemistry Pt. 1.
UCI Chem 1C General Chemistry (Spring 2013) Lec 16. General Chemistry -- Electrochemistry -- Part 1 View the complete course: http://ocw.uci.edu/courses/chem_1c_general_chemistry.html Instructor: Ramesh D. Arasasingham, Ph.D. License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA Terms of Use: http://ocw.uci
From playlist Chemistry 1C: General Chemistry

Kęstutis Česnavičius - Grothendieck–Serre in the quasi-split unramified case
Correction: The affiliation of Lei Fu is Tsinghua University. The Grothendieck–Serre conjecture predicts that every generically trivial torsor under a reductive group scheme G over a regular local ring R is trivial. We settle it in the case when G is quasi-split and R is unramified. To ov
From playlist Conférence « Géométrie arithmétique en l’honneur de Luc Illusie » - 5 mai 2021

NP Completeness II & Reductions - Lecture 16
All rights reserved for http://www.aduni.org/ Published under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike license http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/ Tutorials by Instructor: Shai Simonson. http://www.stonehill.edu/compsci/shai.htm Visit the forum at: http://www.coderisland.c
From playlist ArsDigita Algorithms by Shai Simonson

Introduction to Elliptic Curves 3 by Anupam Saikia
PROGRAM : ELLIPTIC CURVES AND THE SPECIAL VALUES OF L-FUNCTIONS (ONLINE) ORGANIZERS : Ashay Burungale (California Institute of Technology, USA), Haruzo Hida (University of California, Los Angeles, USA), Somnath Jha (IIT - Kanpur, India) and Ye Tian (Chinese Academy of Sciences, China) DA
From playlist Elliptic Curves and the Special Values of L-functions (ONLINE)
Convert Percentages to Fractions
This video explains how to convert percentages to fractions. http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Introduction to Percentages

Minicourse: Deformations of path algebras of quivers with relations. Lecture III
The minicourse consists of 4 lectures. Lecturers: Severin Barmeier and Zhengfang Wang Path algebras of quivers with relations naturally occur throughout representation theory and algebraic geometry — for example in the representation theory of finite-dimensional algebras, as the coordin
From playlist Minicourse: Deformations of path algebras of quivers with relations, JTP New Trends in Representation Theory