Implications and Truth Conditions for Implications
This video defines an implication and when an implication is true or false.
From playlist Mathematical Statements (Discrete Math)

Understanding Logical Statements 1
U12_L1_T2_we1 Understanding Logical Statements 1
From playlist Algebra I Worked Examples
How to determine the inverse of a conditional statement
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a statement. The inverse of a statement is the negation of the hypothesis and the conclusion of a conditional statement. If the hypothesis of a statement is represented by p and the conclusion is represented by q, then the conditional statement is represe
From playlist Inverse of a Statement

How to determine the truth table from a statement and determine its validity
👉 Learn how to determine the truth or false of a conditional statement. A conditional statement is an if-then statement connecting a hypothesis (p) and the conclusion (q). If the hypothesis of a statement is represented by p and the conclusion is represented by q, then the conditional stat
From playlist Conditional Statements

CCSS What are truth tables and how can we create them for conditional statements
👉 Learn how to determine the truth or false of a conditional statement. A conditional statement is an if-then statement connecting a hypothesis (p) and the conclusion (q). If the hypothesis of a statement is represented by p and the conclusion is represented by q, then the conditional stat
From playlist Conditional Statements

Learning to write the inverse of a conditional statement
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a statement. The inverse of a statement is the negation of the hypothesis and the conclusion of a conditional statement. If the hypothesis of a statement is represented by p and the conclusion is represented by q, then the conditional statement is represe
From playlist Inverse of a Statement

2. Ch. 1 (Part 2/3). Introduction to Logic, Philosophy 10, UC San Diego - BSLIF
Video lecture corresponding to _Basic Sentential Logic and Informal Fallacies_, Chapter 1, Part 2 of 3. This is for the class Introduction to Logic, Philosophy 10, UC San Diego.
From playlist UC San Diego: PHIL 10 - Introduction to Logic | CosmoLearning.org Philosophy

How to determine the inverse from a conditional statement
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a statement. The inverse of a statement is the negation of the hypothesis and the conclusion of a conditional statement. If the hypothesis of a statement is represented by p and the conclusion is represented by q, then the conditional statement is represe
From playlist Inverse of a Statement

Recorded: Spring 2014 Lecturer: Dr. Erin M. Buchanan Materials: created for Memory and Cognition (PSY 422) using Smith and Kosslyn (2006) Lecture materials and assignments available at statisticsofdoom.com. https://statisticsofdoom.com/page/other-courses/
From playlist PSY 422 Memory and Cognition with Dr. B

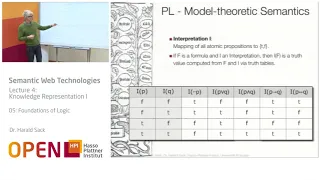
From playlist Semantic Web Technologies by Dr. Harald Sack

Writing the inverse from a conditional statement
👉 Learn how to find the inverse of a statement. The inverse of a statement is the negation of the hypothesis and the conclusion of a conditional statement. If the hypothesis of a statement is represented by p and the conclusion is represented by q, then the conditional statement is represe
From playlist Inverse of a Statement

3. Ch. 1 (Part 3/3). Introduction to Logic, Philosophy 10, UC San Diego - BSLIF
Video lecture corresponding to _Basic Sentential Logic and Informal Fallacies_, Chapter 1, Part 3 of 3. This is for the class Introduction to Logic, Philosophy 10, UC San Diego.
From playlist UC San Diego: PHIL 10 - Introduction to Logic | CosmoLearning.org Philosophy

SEM_013 - Linguistic Micro-Lectures: Implication (Logic)
What is impolication (in logic) and how can the truth-value of propositions connected by logical IF ... THEN be defined? Within just two minutes Prof. Handke discusses and exemplifies the truth-conditions associated with this logical connective.
From playlist Micro-Lectures - Semantics
How to determine the truth of a statement using a truth table
👉 Learn how to determine the truth or false of a conditional statement. A conditional statement is an if-then statement connecting a hypothesis (p) and the conclusion (q). If the hypothesis of a statement is represented by p and the conclusion is represented by q, then the conditional stat
From playlist Conditional Statements

How to determine the truth of a statement using a truth table
👉 Learn how to determine the truth or false of a conditional statement. A conditional statement is an if-then statement connecting a hypothesis (p) and the conclusion (q). If the hypothesis of a statement is represented by p and the conclusion is represented by q, then the conditional stat
From playlist Conditional Statements

12. Ch. 4, Section 4.7. Introduction to Logic, Philosophy 10, UC San Diego - BSLIF
Video lecture corresponding to _Basic Sentential Logic and Informal Fallacies_, Chapter 4, Section 4.7. This is for the class Introduction to Logic, Philosophy 10, UC San Diego.
From playlist UC San Diego: PHIL 10 - Introduction to Logic | CosmoLearning.org Philosophy