
What is the formula to find the sum of an arithmetic sequence
👉 Learn all about series. A series is the sum of the terms of a sequence. Just like in sequences, there are many types of series, among which are: arithmetic and geometric series. An arithmetic series is the sum of the terms of an arithmetic sequence. A geometric series is the sum of the t
From playlist Series

Using sigma sum notation to evaluate the partial sum
👉 Learn how to find the partial sum of an arithmetic series. A series is the sum of the terms of a sequence. An arithmetic series is the sum of the terms of an arithmetic sequence. The formula for the sum of n terms of an arithmetic sequence is given by Sn = n/2 [2a + (n - 1)d], where a is
From playlist Series

Number theory Full Course [A to Z]
Number theory (or arithmetic or higher arithmetic in older usage) is a branch of pure #mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and integer-valued functions. Number theorists study prime numbers as well as the properties of objects made out of integers (for example, ratio
From playlist Number Theory
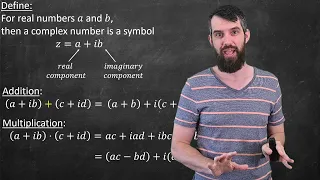
Intro to COMPLEX NUMBERS // Motivation, Algebraic Definition & Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Ep. 1
Welcome to my new series, an Introduction to Complex Numbers. In this Part 1 I give an introduction to the algebraic story. One of the main motivations for studying Complex and Imaginary numbers is just to solve equations like x^2=-1, and much like we defined the number root 2 to be a solu
From playlist Calculus II (Integration Methods, Series, Parametric/Polar, Vectors) **Full Course**
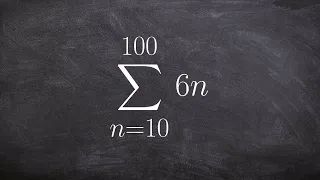
Evaluating the partial sum of a arithmetic series
👉 Learn how to find the partial sum of an arithmetic series. A series is the sum of the terms of a sequence. An arithmetic series is the sum of the terms of an arithmetic sequence. The formula for the sum of n terms of an arithmetic sequence is given by Sn = n/2 [2a + (n - 1)d], where a is
From playlist Series

What is the sum of an arithmetic series using the sum formula
👉 Learn how to find the partial sum of an arithmetic series. A series is the sum of the terms of a sequence. An arithmetic series is the sum of the terms of an arithmetic sequence. The formula for the sum of n terms of an arithmetic sequence is given by Sn = n/2 [2a + (n - 1)d], where a is
From playlist Series
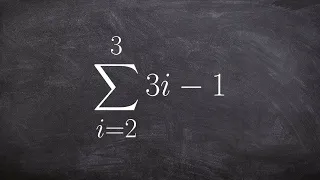
what is sigma notation and how to we use it
👉 Learn how to find the partial sum of an arithmetic series. A series is the sum of the terms of a sequence. An arithmetic series is the sum of the terms of an arithmetic sequence. The formula for the sum of n terms of an arithmetic sequence is given by Sn = n/2 [2a + (n - 1)d], where a is
From playlist Series
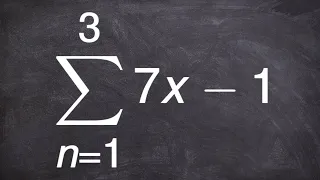
Finding the sum or an arithmetic series using summation notation
👉 Learn how to find the partial sum of an arithmetic series. A series is the sum of the terms of a sequence. An arithmetic series is the sum of the terms of an arithmetic sequence. The formula for the sum of n terms of an arithmetic sequence is given by Sn = n/2 [2a + (n - 1)d], where a is
From playlist Series

LMS Popular Lecture Series 2009, Random Matrices and Riemann Zeros, Dr Nina Snaith
Hollywood's Hippest Mathematics: random matrices and Riemann zeros Dr Nina Snaith
From playlist LMS Popular Lectures 2007 - present
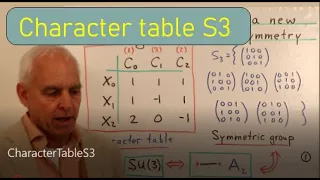
The S3 character table - a (somewhat) new meaning | Diffusion Symmetry 2 | N J Wildberger
With diffusion symmetry, we explore mathematical objects or physical systems by spreading or diffusing from an initial point. The algebraic objects that result are hypergroups, or fusion algebra, or one of many similar and almost equivalent systems found in combinatorics, group theory, num
From playlist Diffusion Symmetry: A bridge between mathematics and physics

Maths Skills: Mathematical Induction
This video is a beginner's guide to mathematical induction. We give a step-by-step explanation of why it works, and then try it out with an easy example. Another useful dose of Maths for everyone by Dr Sarada Herke. Link to other videos: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A2ccjnEFQGU - Math
From playlist Maths Skills

Advice for prospective research mathematicians | Rational Trigonometry and spread polynomials 1
Here is a quick introduction / review of the essentials of Rational Trigonometry, with an aim to explaining the important spread polynomials / polynumbers which are more pleasant variants of the Chebyshev polynomials of the first kind. Our treatment here is quite concise, relying on a pri
From playlist Maxel inverses and orthogonal polynomials (non-Members)

Elchanan Mossel - Some mathematical theorems on agreement and learning in networks - IPAM at UCLA
Recorded 16 February 2022. Elchanan Mossel of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology presents "Some mathematical theorems on agreement and learning in networks" at IPAM's Mathematics of Collective Intelligence Workshop. Learn more online at: http://www.ipam.ucla.edu/programs/workshops/m
From playlist Workshop: Mathematics of Collective Intelligence - Feb. 15 - 19, 2022.

3D Gauge Theories: Vortices and Vertex Algebras (Lecture 1) by Tudor Dimofte
PROGRAM: VORTEX MODULI ORGANIZERS: Nuno Romão (University of Augsburg, Germany) and Sushmita Venugopalan (IMSc, India) DATE & TIME: 06 February 2023 to 17 February 2023 VENUE: Ramanujan Lecture Hall, ICTS Bengaluru For a long time, the vortex equations and their associated self-dual fie
From playlist Vortex Moduli - 2023

7 8 Pricing options on more underlyings Part 2
BEM1105x Course Playlist - https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL8_xPU5epJdfCxbRzxuchTfgOH1I2Ibht Produced in association with Caltech Academic Media Technologies. ©2020 California Institute of Technology
From playlist BEM1105x Course - Prof. Jakša Cvitanić
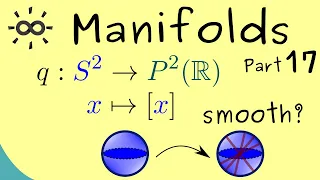
Manifolds - Part 17 - Example of Smooth Maps
Support the channel on Steady: https://steadyhq.com/en/brightsideofmaths Or support me via PayPal: https://paypal.me/brightmaths Or via Ko-fi: https://ko-fi.com/thebrightsideofmathematics Or via Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/bsom Or via other methods: https://thebrightsideofmathematics.
From playlist Manifolds

Topology - Crosscaps and Handles: Oxford Mathematics 2nd Year Student Lecture
In this lecture from our 2nd year Topology course, Andre Henriques describes crosscaps and handles in a visual way. He relies both on detailed beautiful pictures, and also on precise equations. Crosscaps and handles are the building blocks of all surfaces: any compact surface can be obtain
From playlist Oxford Mathematics Student Lectures - Topology

Advanced Knowledge Problem of the Week 5-19-16
In this video, Chloe explains how to prove that the intersection of two subsets of V is also a subset of V. For the full problem and solution transcript, visit our blog: http://bit.ly/1XmMqVh
From playlist Center of Math: Problems of the Week

Even more DFAs: Theory of Computation (Feb 3 2021)
One more examples of DFAs, plus the formal description. This is a recording of a live class for Math 3342, Theory of Computation, an undergraduate course for math & computer science majors at Fairfield University, Spring 2021. Class website: http://cstaecker.fairfield.edu/~cstaecker/cou
From playlist Math 3342 (Theory of Computation) Spring 2021
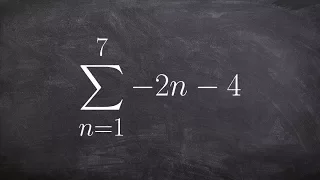
Learn to use summation notation for an arithmetic series to find the sum
👉 Learn how to find the partial sum of an arithmetic series. A series is the sum of the terms of a sequence. An arithmetic series is the sum of the terms of an arithmetic sequence. The formula for the sum of n terms of an arithmetic sequence is given by Sn = n/2 [2a + (n - 1)d], where a is
From playlist Series